Journal of Daylighting
An international journal devoted to investigations of daylighting in buildings. It is the leading journal that publishes original research on all aspects of Energy, buildings, and lighting.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
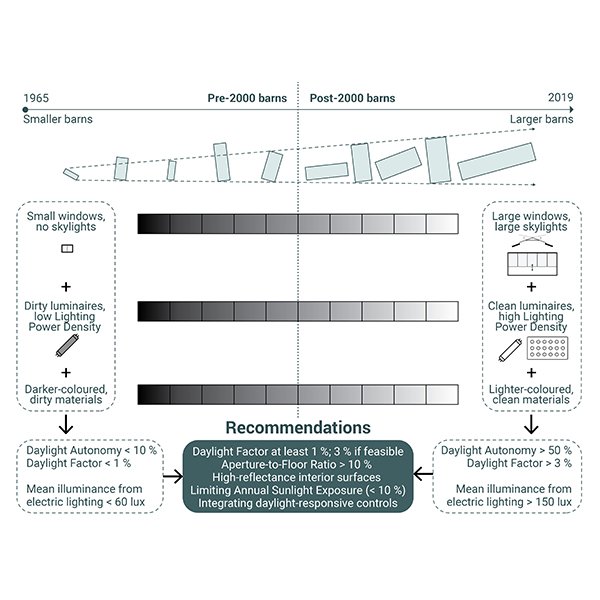
Architectural Factors Affecting Illumination in Swedish Dairy Barns: Insights from
Illumination of dairy barns impacts animal health, milk production, and building energy efficiency. The aim of this study was to assess the existing daylighting and electric lighting conditions of dairy barns located in Southern Sweden.
Journal of Daylighting 13 (2026) 108-123
RESEARCH ARTICLE
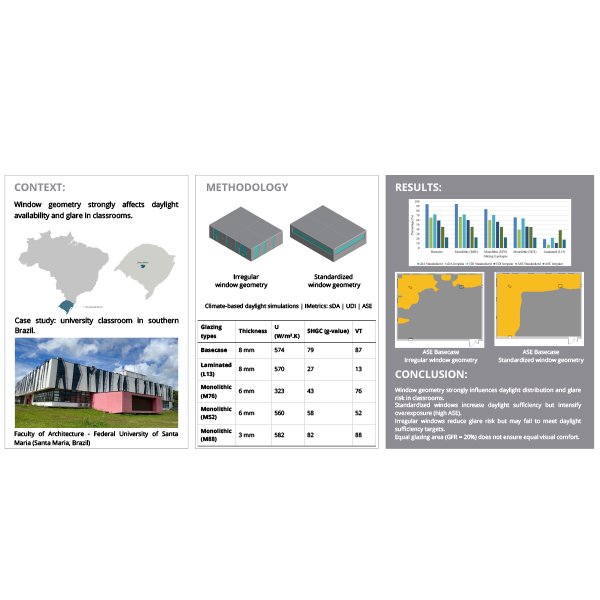
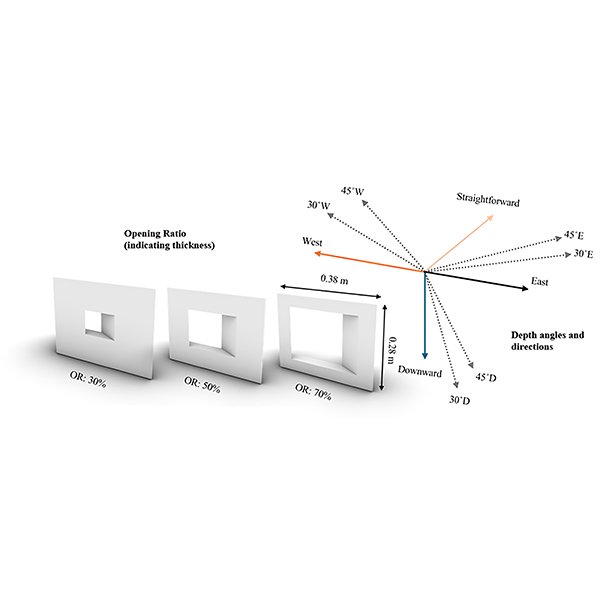
Evaluating Daylighting Gains from Window Geometry Reconfiguration in a Classroom
Daylighting is a key aspect of educational building design, supporting both visual comfort and energy efficiency. However, design practice often reduces the role of windows to aperture ratios, with limited attention to the influence of window geometry on daylight performance.
Journal of Daylighting 13 (2026) 97-107
RESEARCH ARTICLE
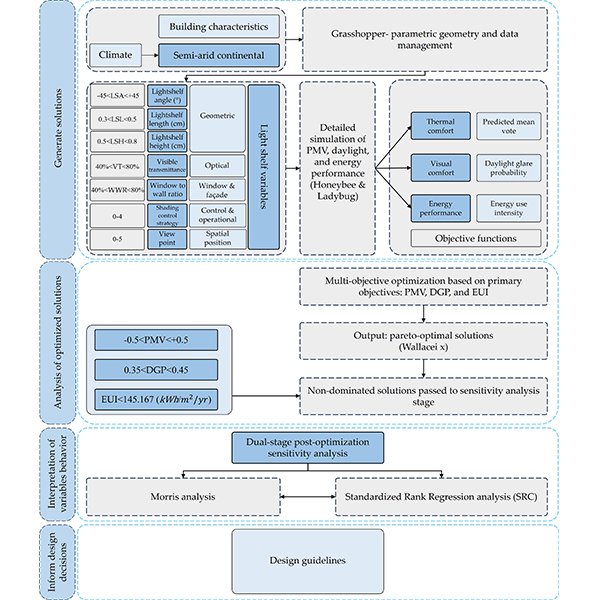
Sequential Multi-Objective Optimization and Post-optimization Sensitivity Analysis of
Global climate action necessitates the optimization of building envelopes during early design to enhance energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Exterior light shelves are a critical passive strategy for improving thermal and visual comfort while simultaneously reducing energy consumption.
Journal of Daylighting 13 (2026) 76-96
REVIEW ARTICLE
Daylight Enhancement Strategies for Historic Buildings: A Critical Review of
With the growing urgency to reduce carbon emissions in the built environment, enhancing daylight availability in historic buildings has become a critical and challenging task due to the required balance between environmental sustainability objectives and cultural heritage conservation principles.
Journal of Daylighting 13 (2026) 57-75
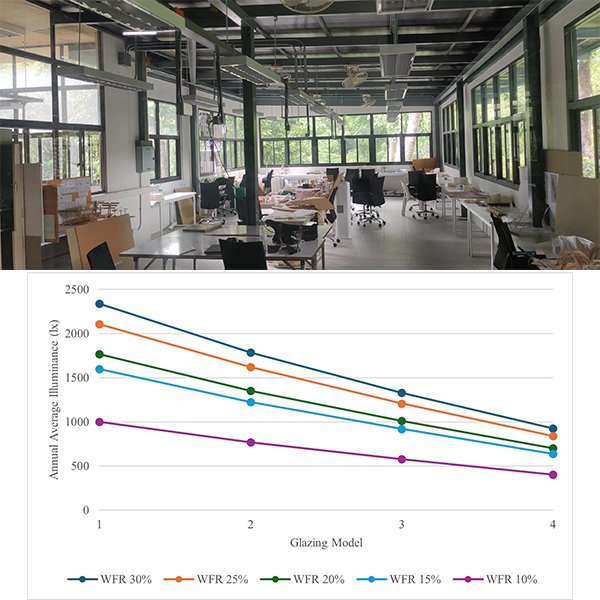
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimizing Window-to-Floor Ratio and Glazing for Daylight and
In tropical climates, where cooling loads dominate building energy use, minimizing cooling demand is particularly critical for achieving carbon neutrality in educational buildings while maintaining adequate daylight and visual comfort.
Journal of Daylighting 13 (2026) 44-56
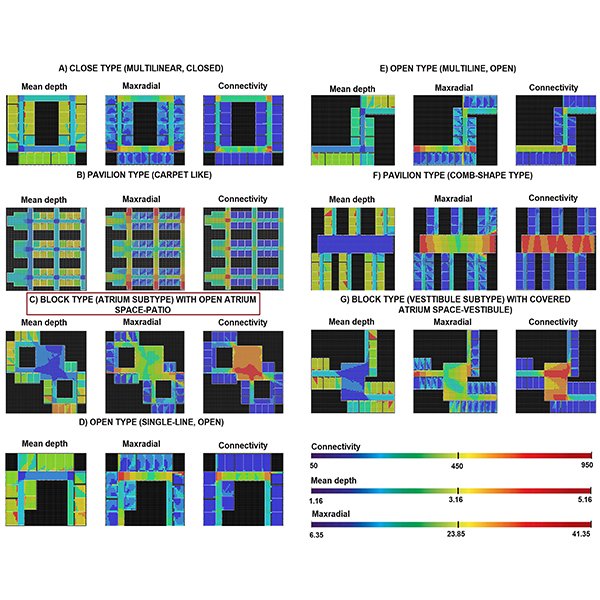
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Comparative Analysis of Daylight and Visual Quality Across School Plan
Designing daylight-based spaces has gained increasing attention due to its numerous benefits and alignment with global sustainability standards. However, limited research has focused on how architectural layouts affect daylight distribution and visual quality, particularly in educational environments.
Journal of Daylighting 13 (2026) 20-43
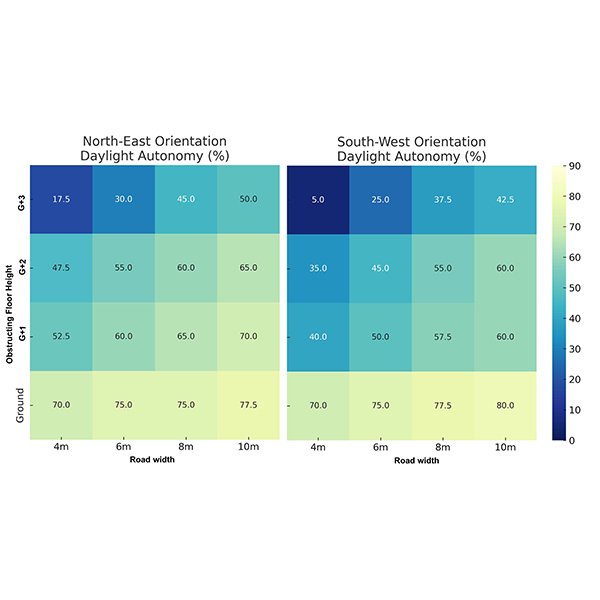
RESEARCH ARTICLE
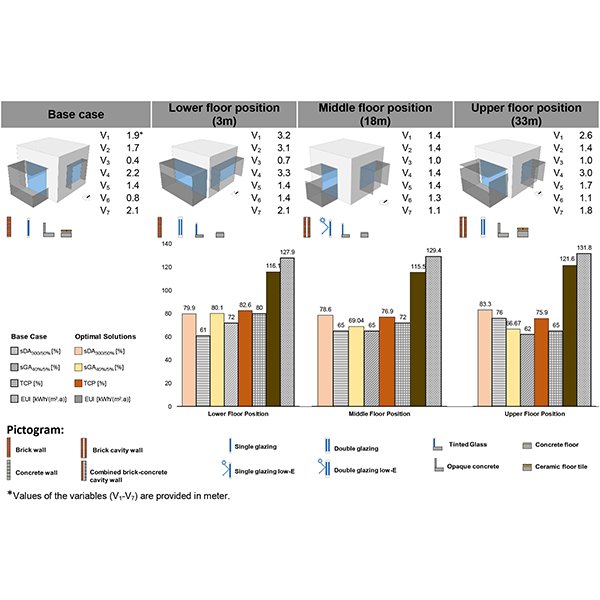
Effects of Urban Obstructions on Spatial Daylight Autonomy (sDA) and
The limited research on obstruction-driven daylight reduction continues to hinder efforts to optimize natural daylight in compact mid-rise residential buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 13 (2026) 1-19
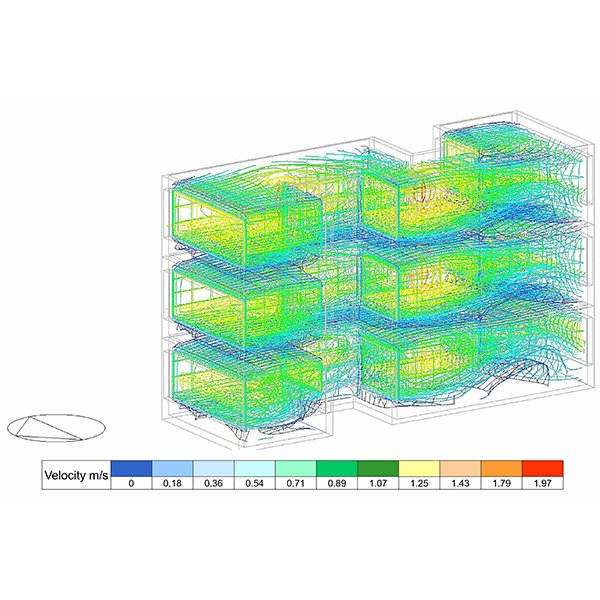
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Integration of light well through generative design to achieve optimal
A case of urban densification in heritage towns like Pondicherry has led to deep-plan wall to wall layouts, where the depth of the plot is considerably more than its width and multi-storey buildings with limited access to day light and natural ventilation.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 548-560
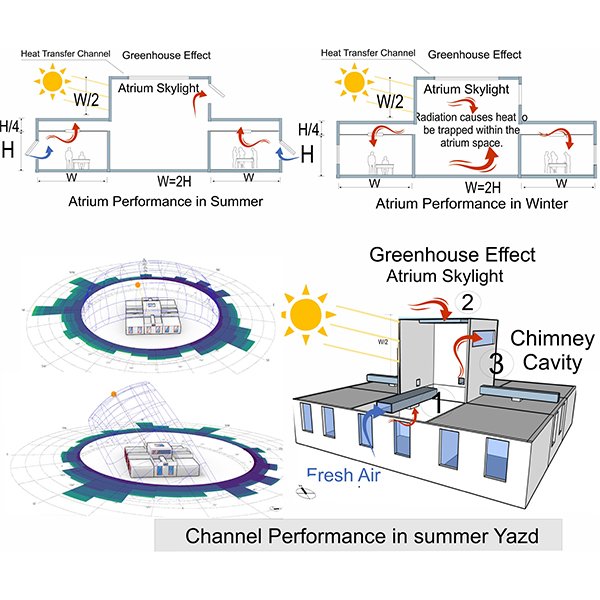
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design Optimization of Atrium Skylights for Enhanced Office Building Performance
The increasing demand for energy and the impact of climate change underscore the necessity of energy-efficient building designs. This study optimizes atrium skylights as a passive design solution for Yazd, Iran aiming to enhance thermal and visual comfort.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 520-547
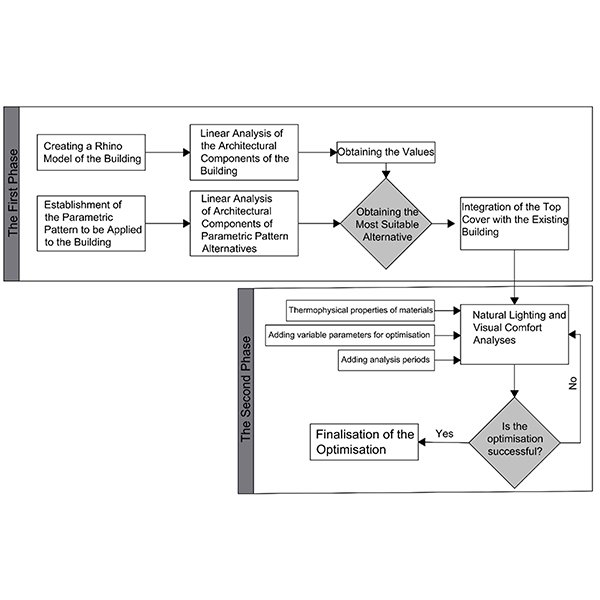
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Parametric Exploration of Natural Lighting and Visual Comfort in Contemporary
The re-functioning of historical buildings frequently necessitates new additions. This is particularly relevant for historical buildings with open courtyards, where interventions often involve the installation of upper covers using contemporary materials and techniques This issue can become especially apparent in historical buildings that are completely enclosed with transparent materials, raising concerns about the greenhouse effect and its potential to compromise indoor comfort.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 506-519
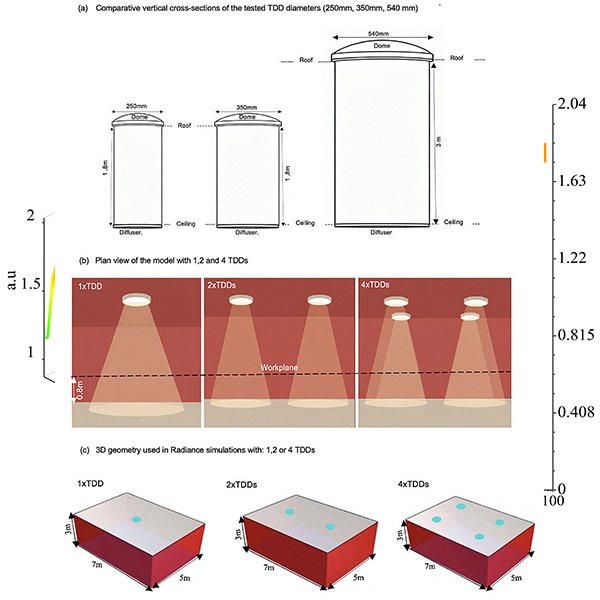
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Multi-Criteria Optimization of Tubular Daylighting Devices for Classrooms in
In educational architecture, particularly in high-solar climates, achieving a balance between ample daylight and visual comfort is a significant challenge.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 491-505
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Multi-objective Optimization of Girih Tile Patterns and Colored Glass
Efficient energy use is vital in architecture, and the building envelope plays a key role in aesthetics, thermal comfort, energy efficiency, and natural lighting.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 441-467
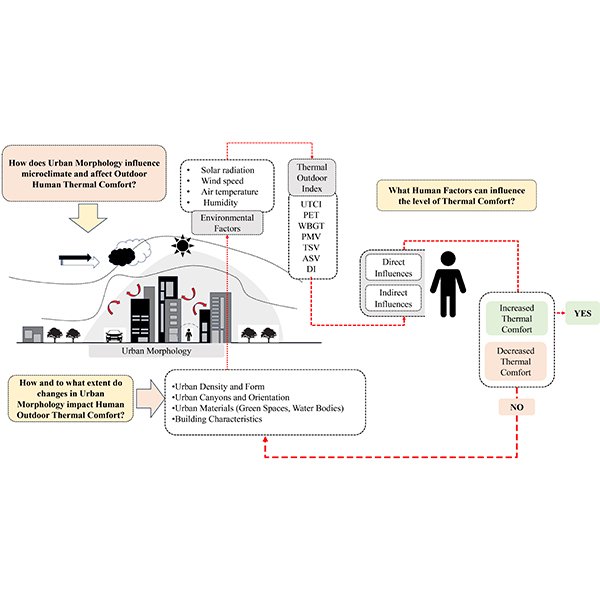
REVIEW ARTICLE
Human Interaction with Urban Morphology under the Influence of Urban
Outdoor urban spaces are essential to residents’ well-being, yet their thermal comfort is increasingly compromised by urbanization and climate change. .
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 468-490
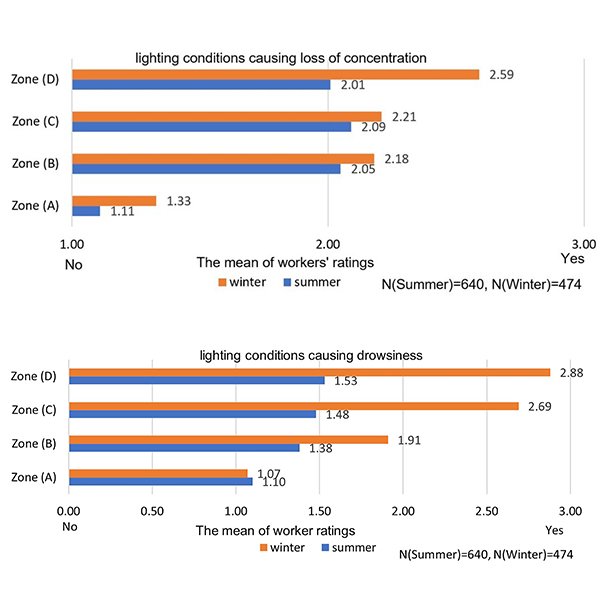
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluating the Impact of Lighting Conditions on Workers’ Safety and
Lighting is a key element of design that plays a significant role in affecting workers’ health and safety in industrial workspaces. Given the scarcity of scientific studies addressing visual environments in relation to workers health in industrial buildings, this field study was conducted to explore workers' responses to multiple lighting scenarios inside production halls on their occupational health and safety in six factories in Sadat City, Egypt. .
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 420-440
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluating Daylighting Performance of Parametric Mashrabiya in Mediterranean Climate: A
This study examines the daylighting performance of parametric Mashrabiya-inspired shading devices in a Mediterranean climate, aiming to enhance occupant comfort and visual performance.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 397-419
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Height-Responsive Balcony-Integrated Envelope Design for High-Rise Residential
Balconies function as essential shading elements within the building envelope, playing a critical role in regulating occupant comfort and energy efficiency.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 375-396
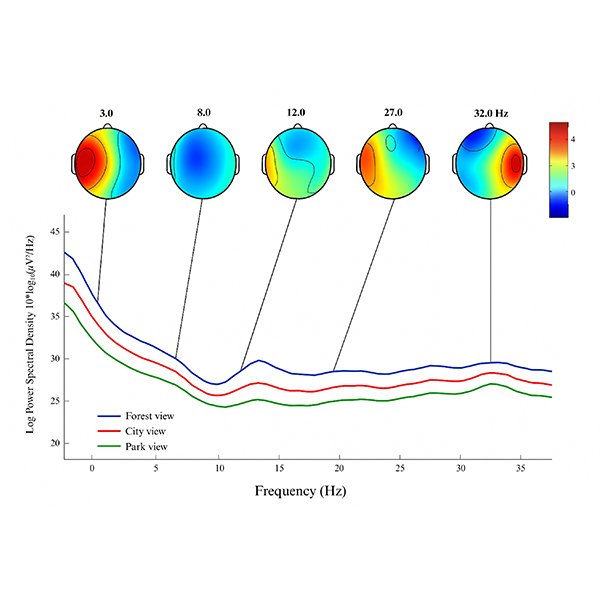
RESEARCH ARTICLE
EEG-Based Neurophysiological Responses to Classroom Window Views in Green
This study examines the neurophysiological responses of students to different classroom window views - forest, park, and city - within energy-efficient, green campus environments.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 359-374
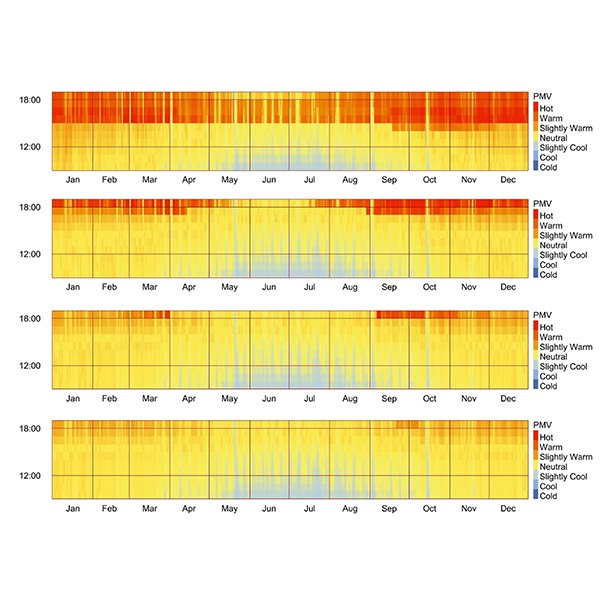
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Enhancing Year-Round Thermal Comfort with Solar Control Films: A
Windows significantly contribute to thermal discomfort in high solar irradiance climates by allowing excessive heat gains and uneven indoor temperatures.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 343-358
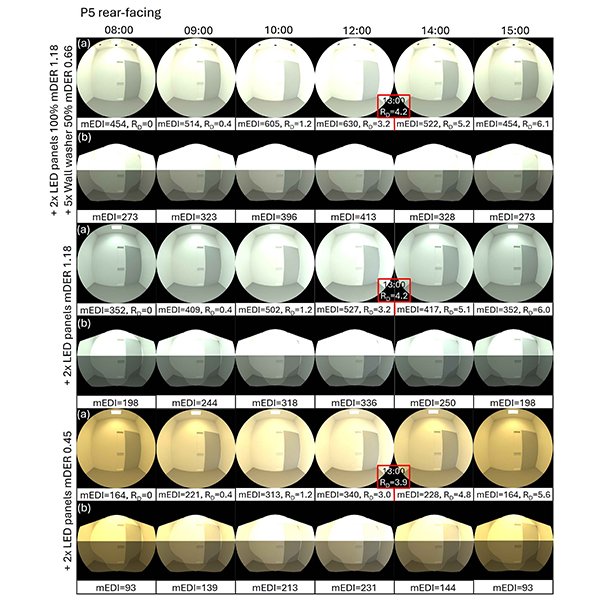
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluating Visual and Beyond-Vision Light Effects and Energy Consumption
Light influences human physiology and psychology through visual and beyond-visual effects, collectively termed ‘integrative lighting.’ Human responses depend on luminous (quantity, spectrum, directionality) and temporal (timing, duration, history) factors, yet no studies examined their combined influence on integrative lighting. Th.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 306-342
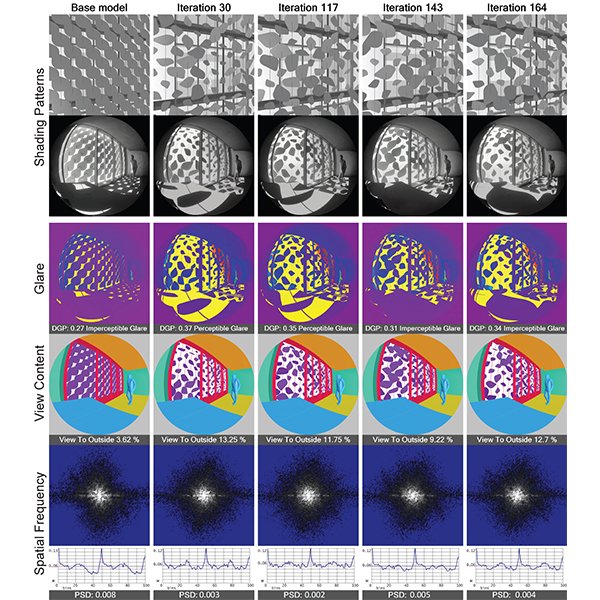
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Occupant-Centric Visual Comfort Assessment and Optimization of Passive Solar
This study introduces a comprehensive computational framework integrating image-based simulations, spatial frequency analysis, and multi-objective optimization to evaluate and optimize passive solar shading devices from an occupant-centric perspective.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 293-305

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design Alternatives of Light Shelves using Altmann Linkage
This paper proposes a novel new light shelf design with Altmann linkage using its kinetic principles: geometry and rotational angles. As previous studies explain a light shelf’s design in two ways: static and movable, the proposed one in this study has the potential to track the path of the sun due to its diagonal movement. .
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 391-407
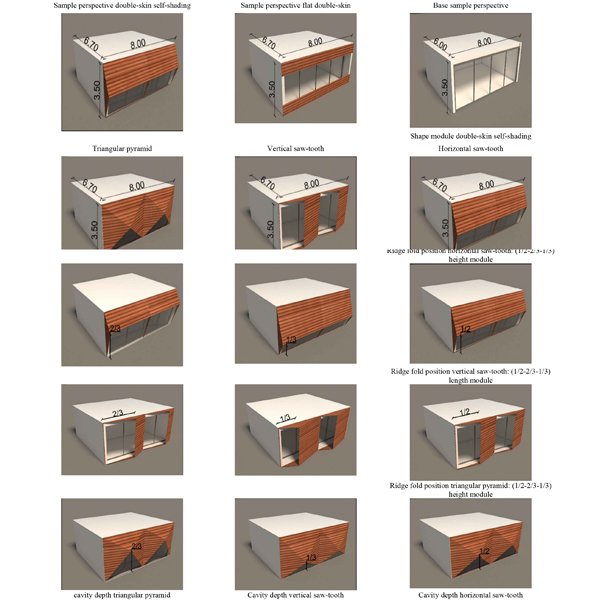
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimum Geometry of Double-skin Self-Shading Facade of Classrooms
The significant energy consumption in educational spaces worldwide and its environmental impact greatly influence the quality of space, learning levels, and student comfort.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 372-389
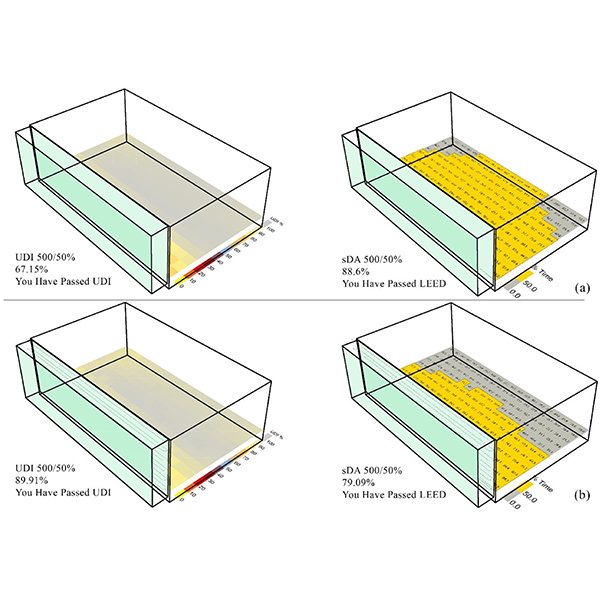
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Parametric Optimization Approach to Evaluate Dynamic Shading Within Double-Skin
This research aims to support the choice of an appropriate dynamic louver shading system (DL-SS) within double-skin facade insulated glazed units (DSF-IGUs) as a high-performance integrated window system (DSF-IGUs/DL-SS) that meets both thermal and energy performance via daylight availability under a tropical climate.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 349-371
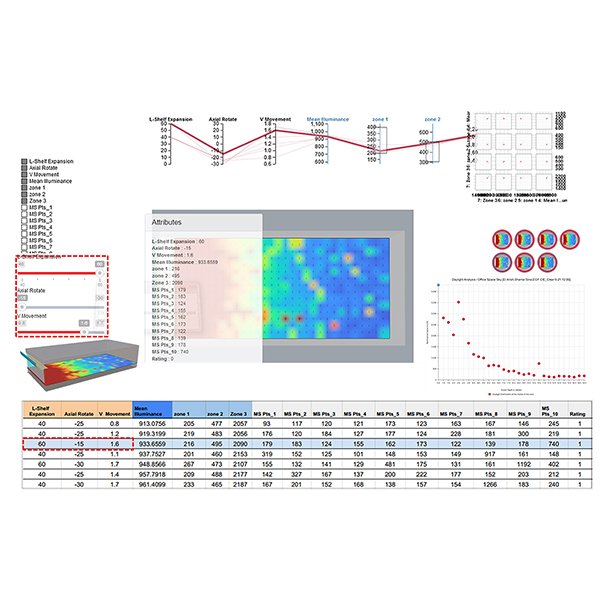
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Artificial Neural Network to Predict Curvature Light Shelf Design Related
Energy Optimization in building design field now has been revolutionized due to AI and machine learning applications. Leveraging daylight to reduce artificial lighting consumption holds promise for significant energy savings, yet the nonlinear nature of daylight patterns poses challenges in prediction and optimization.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 334-348
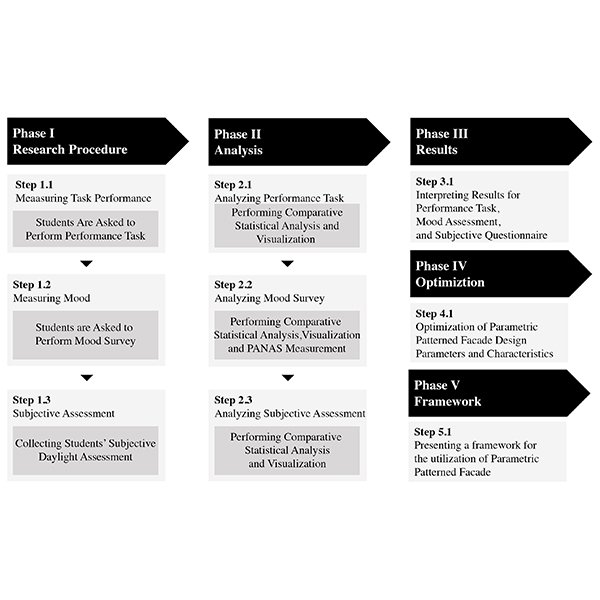
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Investigation of the Effect of Parametric Patterned Façade and
Parametric design is one of the thriving contemporary architectural treatments that not only has an influence on the design of building envelopes but is capable of affecting the users physically and psychologically.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 312-333
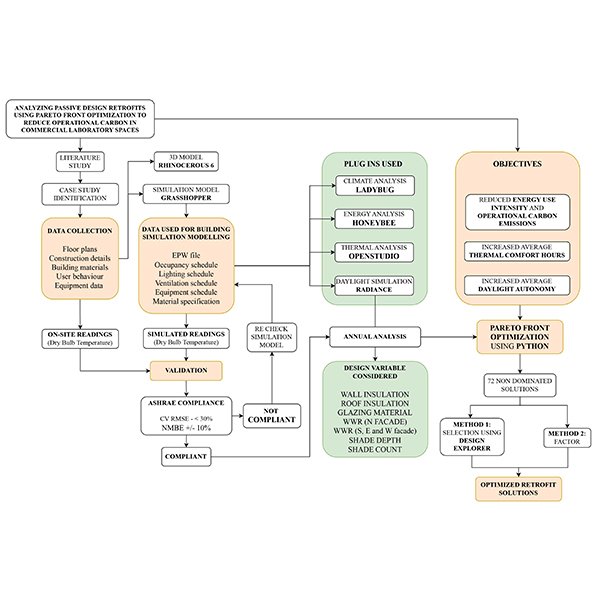
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Analyzing Passive Design Retrofits using Pareto Front Optimization to Reduce
Buildings are one of the leading sources of carbon emissions in the world. Most of the carbon emissions are released during the operation phase of the building.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 290-311
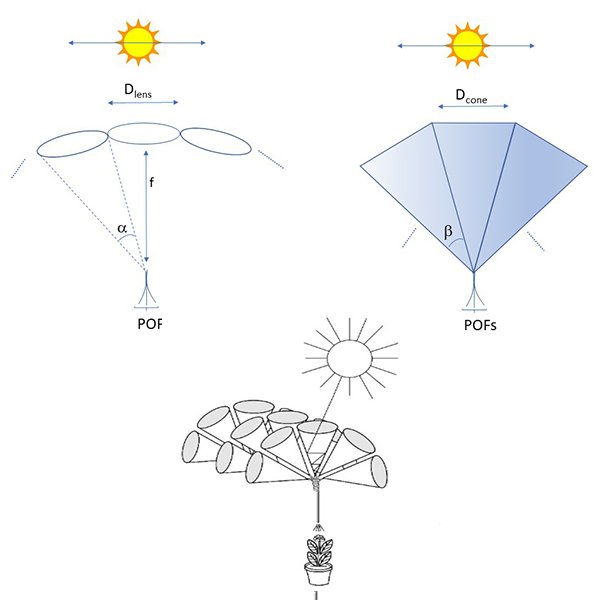
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Tracker-less Sunlight Collection Apparatus, using an Array of Optical
The paper describes an array of optical cones as a potential configuration for tracker-less daylighting, without using an electro-mechanical tracker. Subsequently, a single optical cone is analyzed, mainly in terms of sunlight collection efficiency and acceptance angle, as a function of the cone's geometrical dimensions.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 279-289
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Analytical Study on Reducing the Heating Effects of Daylight and
Climate change is an environmental issue that is rapidly escalating due to the effects of global warming. The increase in carbon emissions, along with various human activities such as industrial processes, land use changes, and the reckless consumption of natural resources, are among the primary causes of global warming.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 268-278
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimising Daylighting Performance Through Side light with Passive Devise Design
Passive lighting design plays an important role in providing natural lighting to save electricity consumption in buildings. This study aims to investigate the performance of natural lighting and the potential of alternative designs through sidelights with 3 shading device models and light shelves with different sizes in north, west, east, and south orientations.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 247-267
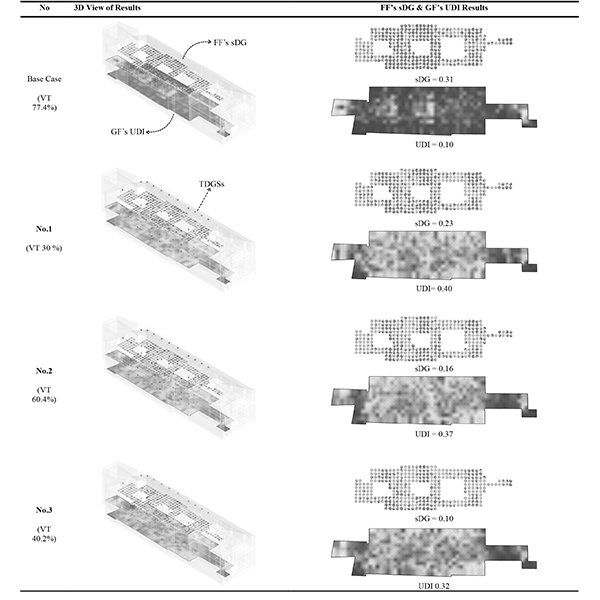
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylight Enhancement Strategies Through Roof for Heritage Buildings
Enhancing daylighting in heritage buildings is a complex challenge that requires a delicate balance between preserving architectural integrity and improving visual comfort.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 234-246
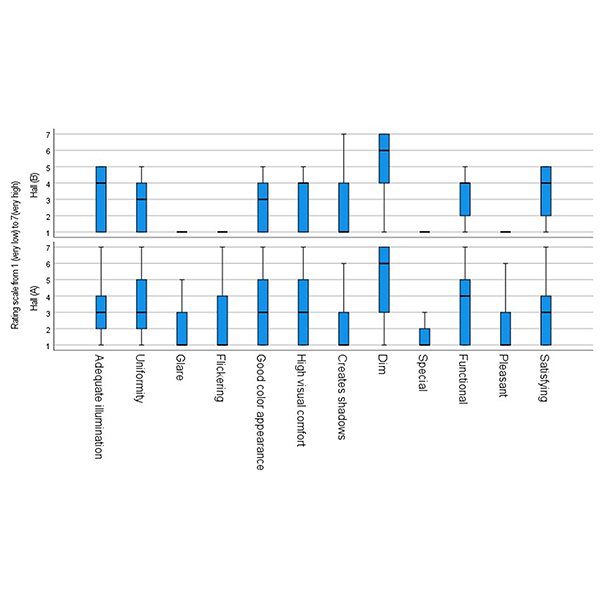
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Investigation of daylight availability in university dining halls: A case
This study evaluates the availability of daylight inside a university’s dining halls over two days (one sunny and one cloudy) using light meters in real-life sittings. .
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 216-233
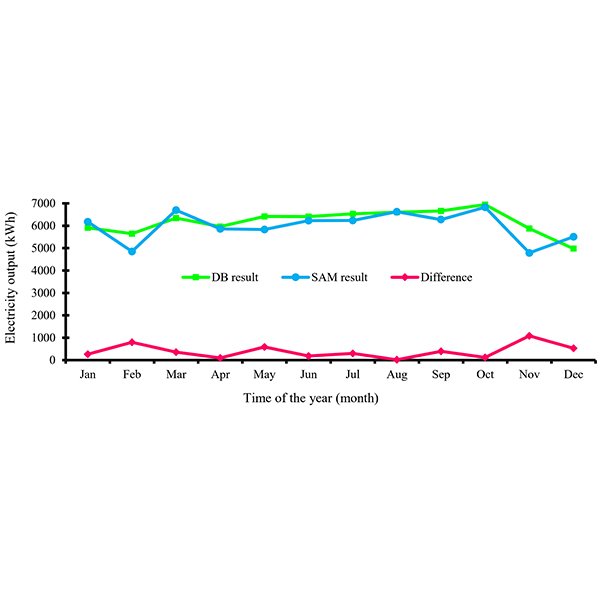
RESEARCH ARTICLE
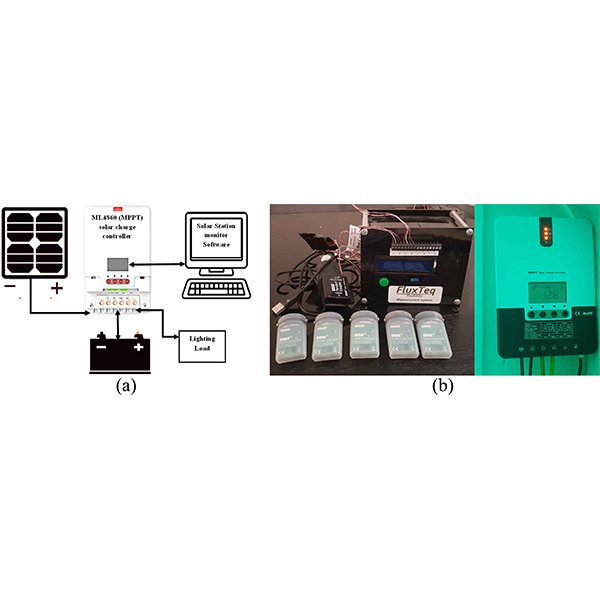
Energy efficiency in smart schools using renewable energy strategy
As smart schools increasingly rely on technology, achieving energy efficiency becomes crucial for cost reduction and sustainability. This study investigates energy efficiency strategies in smart schools, focusing on the integration of renewable energy technologies.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 203-215
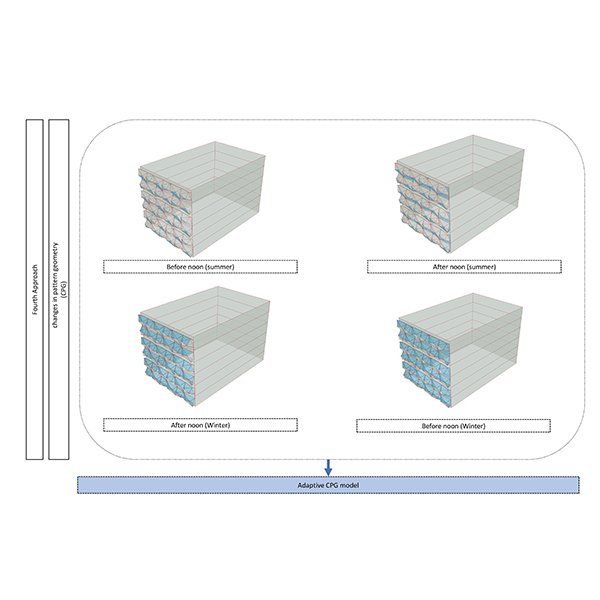
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Synergistic Strategies: Comparing Energy Performance in Climate-Adaptive Building Envelopes
Climate change and improving building energy performance are significant contemporary concerns. Conversely, climate-adaptive building envelopes (CABEs) offer promising solutions to enhance structural performance amidst fluctuating environmental conditions.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 181-202
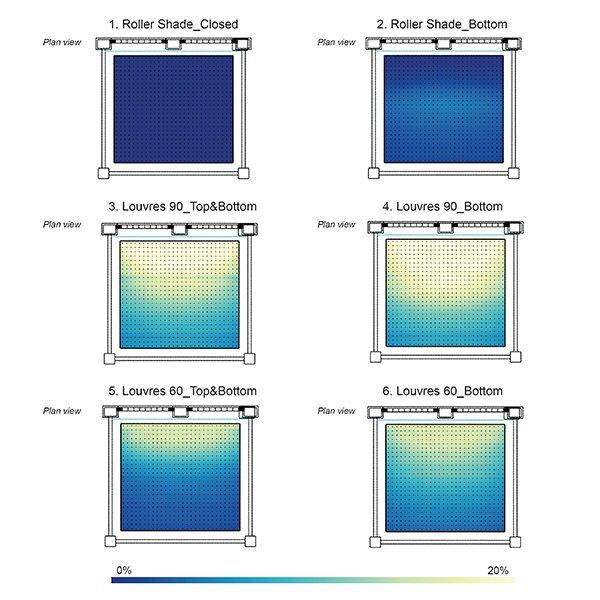
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design Adjustments For Daylighting and Visual Comfort in a Classroom
This paper evaluates how design adjustments applied to roller shades and louvres (namely the height of the shadings head and the angles of the louvre slats) can improve their annual and spatial effectiveness to provide autonomous daylight levels, reduce daylight glare problems, and offer views outside.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 165-180
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Performance of Shading Against West Glass Facades to Optimise Daylight,
In tropical urban areas, the vertical facades of buildings often play a crucial role in capturing solar radiation and heat, especially for office buildings facing west during the afternoon.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 131-148
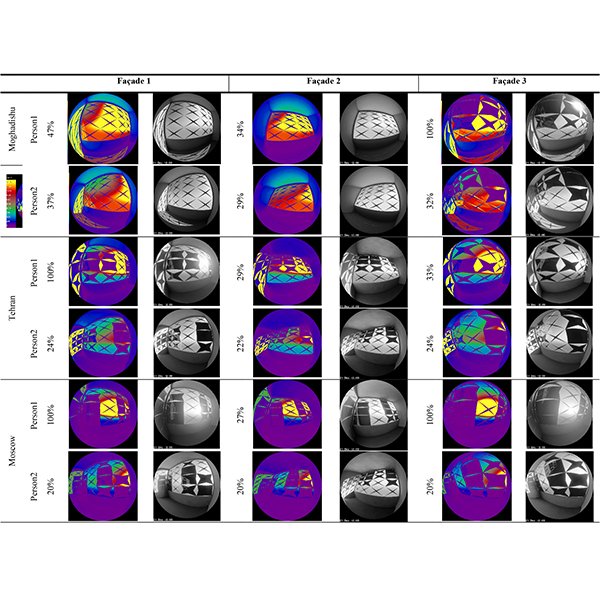
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Designerly Approach to Design Responsive Façade for Occupant Visual
In recent years, attention has focused on improving the health and satisfaction of employees by enhancing visual comfort in workplaces. This involves providing adequate natural daylight, glare control, and outdoor views.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 149-164
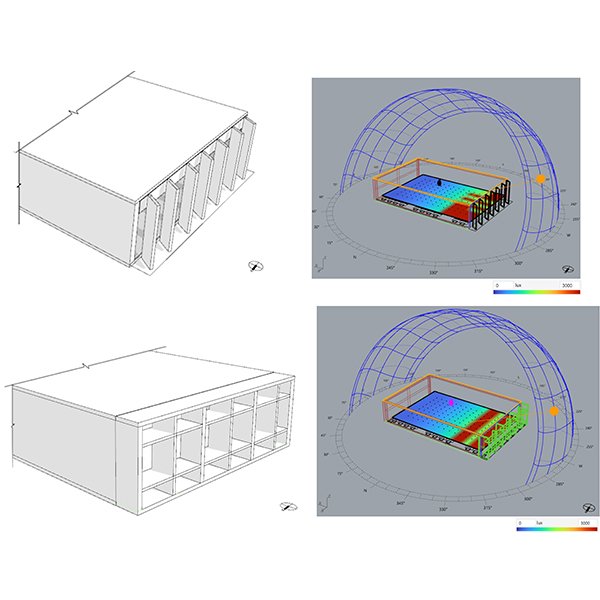
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Geometry Optimization of Industry Buildings for Energy-Driven Design Development
Even though the manufacturing industry consumes roughly 54% of total available energy globally, little consideration has been devoted to optimizing energy in the early stages of industry design, particularly in densely populated cities.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 119-130
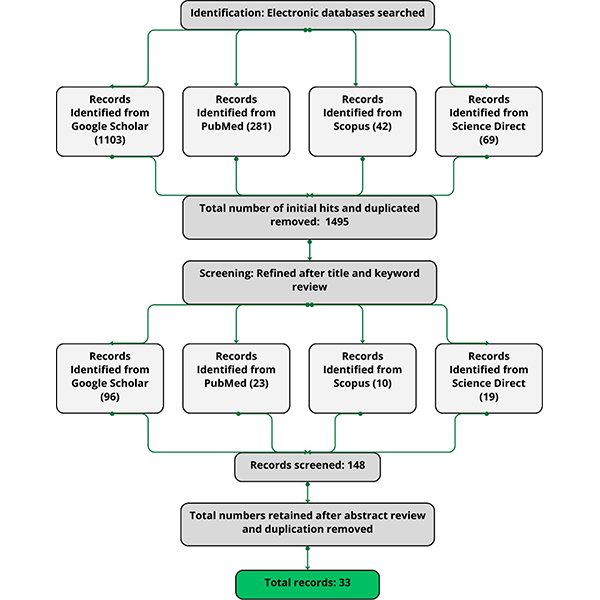
REVIEW ARTICLE
Exploring Methodological Considerations: A Literature Review on How Lighting Affects
The impacts of lighting conditions on human circadian rhythms, sleep quality, and cognitive performance have been extensively investigated in the past two decades; however, these studies have yielded inconclusive and variable outcomes.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 97-118

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Enhancing Visual Comfort and Energy Efficiency in Office Lighting Using
The number of desk workers who frequently conduct their jobs at home has increased dramatically during Covid-19. Work-from-home flexibility makes it attractive for workers and companies, resulting in a “Work-Style Reform” after the Covid-19 pandemic. Ho.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 69-96
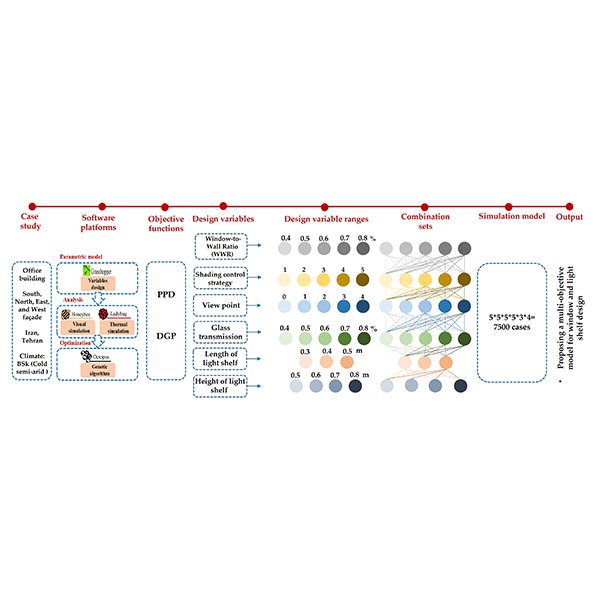
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Multi-objective Optimization of Window and Light Shelf Design
In office buildings, an efficient design of windows and using light shelves as a passive design strategy significantly influence the thermal and visual comfort of occupants while enhancing the productivity and health of users.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 55-68
Join our Editorial Board
CVs should be submitted electronically to jd@solarlits.com.
Editorial Board

Prof. Lambros T. Doulos
Hellenic Open University, Greece

Dr Guiqiang Li
University of Science and Technology of China, China

Prof Umberto Berardi
Politecnico di Bari, Italy

Prof. Barbara Szybinska Matusiak
NTNU, Norway

Dr Paola Sansoni
CNR-INO, Italy

Dr Susana Lagüela López
University of Vigo, Spain

Dr Ferdinando Salata
University of Rome, Italy

Prof. Nabil Elminshawy
Port Said University, Egypt

Dr Boon Han Lim
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Malaysia

Prof. Yuehong Su
University of Nottingham, UK

Prof. Önder Güler
Istanbul Technical University, Türkiye

Prof Laura Bellia
University of Naples Federico II, Italy

Dr Fabio Peron
IUAV University of Venice, Italy

Prof Francesco Asdrubali
University of Perugia, Italy

Dr. Kacem Gairaa
center for renewable energy development, Algeria

Prof Jitka Mohelnikova
Brno University of Technology, Czech Republic

Faris Ali Mustafa
Salahaddin University - Erbil, Iraq

Dr Vincenzo Costanzo
University of Catania, Italy

Wei Wang
Southeast University, 中国

Dr. Francesca Fragliasso
University of Naples Federico II, Italy

Dr Paula M. Esquivias
University of Granada, Spain

Omid Nematollahi
Isfahan University of Technology, South Korea

Dr. Michele Rocca
University of Pisa, Italia

Dr Francesco Sommese
University of Naples Federico II, italy

Dr. Feride Şener Yılmaz
Istanbul Technical University, Turkey

Dr Lim Yaik Wah
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia

Dr Petar Pejic
University of Niš, Serbia

Dr Hui Lv
Hubei University of Technology, China

Dr Karam M. Al-Obaidi
Sheffield Hallam University, UK

Dr Mohammed Salah Mayhoub
Al-Azhar University, Egypt
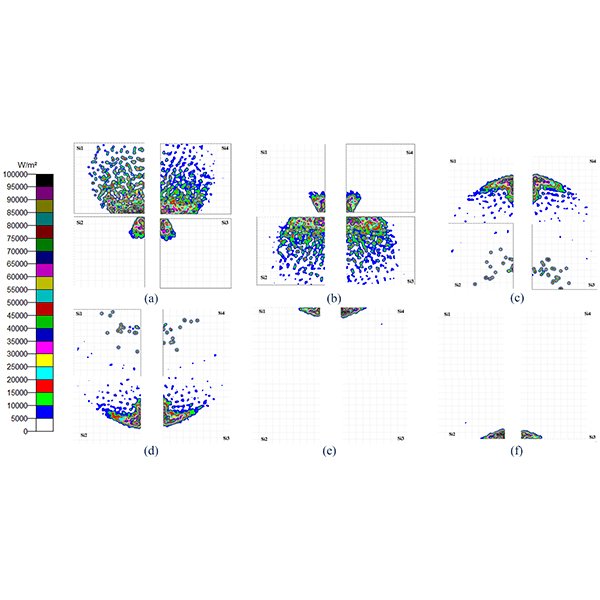
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Improvement of Optical Performances Using the Hybrid CPV
Hybrid Concentrated Photovoltaics (HCPVs) are systems in which additional low-cost silicone solar cells are added to take advantage of the power generated by the diffuse radiation lost when using only multi-junction cells that work only with direct radiation.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 238-245

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Comparative Study on Computer Simulation of Solar Shading Performance with
Current technological advancement and the requirement for sustainability-driven practices has birthed increased demands for accuracy in performance and assessment of energy consumption in the built environment.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 50-64

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylight Distribution Improvement Using Automated Prismatic Louvre
Louvre is a common type of shading devices and has been increasingly used in office buildings. Meanwhile, some reflective types of louvre have been used to provide shade and to redirect daylight deep into buildings interior simultaneously.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 84-92

REVIEW ARTICLE
Daylight in Buildings and Visual Comfort Evaluation: the Advantages and
Exposure to daylight significantly affects the psychological well-being of occupants by diminishing headaches, eye tensions, or stress. Daylight penetration is a matter of collaboration between building façade and perimeter zones that can be controlled through façade design features. .
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 181-203
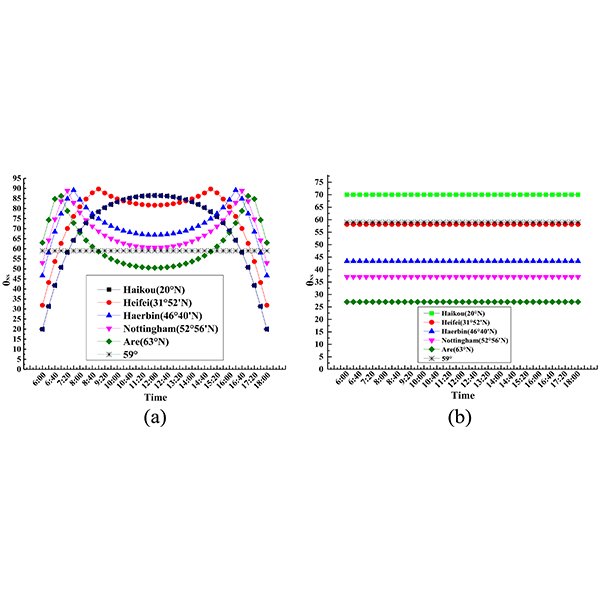
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design and optical evaluation of a novel asymmetric lens-walled
Solar concentrating system is an effective way of combing solar energy with the building to satisfy the needs besides of electricity and hot water, also includes building heating, refrigeration, dehumidification, which require higher quality heat source.
Journal of Daylighting 4 (2017) 26-37

RESEARCH ARTICLE
A New Trend for Indoor Lighting Design Based on A
Most power system planners are interested in the savings of electrical power consumption. Various references demonstrate that the highest consumed power is by the lighting systems standing around 19% of worldwide energy consumption.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 137-153
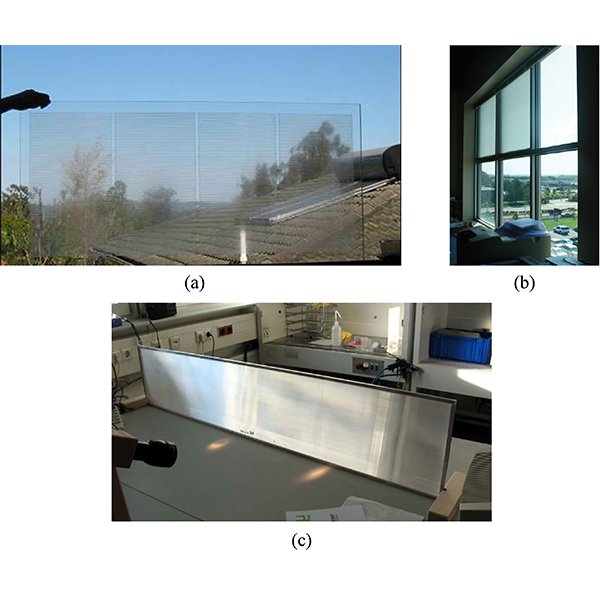
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Annual Performance Assessment of Complex Fenestration Systems in Sunny Climates
Complex Fenestration Systems (CFS) are advanced daylighting systems that are placed on the upper part of a window to improve the indoor daylight distribution within rooms.
Journal of Daylighting 2 (2015) 32-43

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Visual Comfort Assessment of Hospital Patient Rooms with Climate Responsive
As advanced technologies become prevalent, they are being used more widely in numerous fields. The building sector is not an exception. One of these cutting-edge technologies is responsive facades, which are used in buildings and have an undeniable effect on daylighting.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 17-30
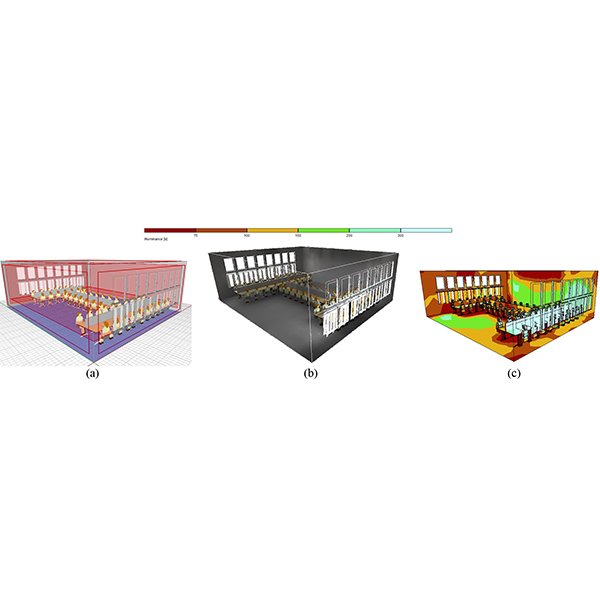
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Parametric Analysis of Architectural Elements on Daylight, Visual Comfort, and
The quality of visual comfort has always been an essential element considering human comfort. Providing visual comfort in a living environment reduces the need for artificial lighting, which subsequently has a direct relationship with energy consumptions and its expenses.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 57-72
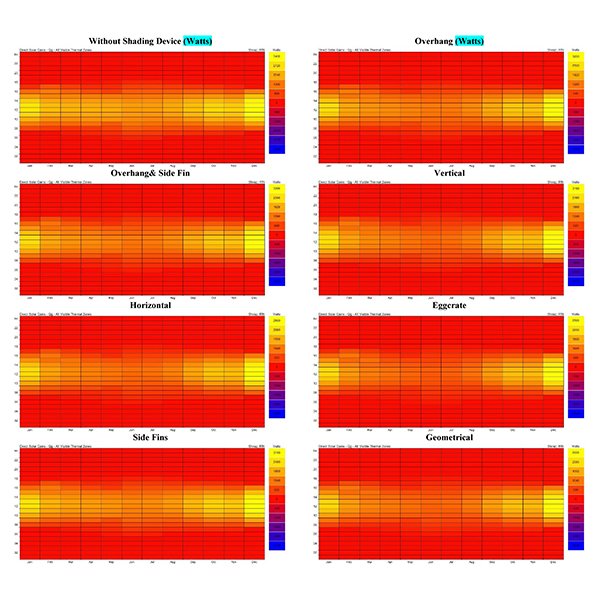
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Effect of Fixed External Shading Devices on Daylighting and
Building shading devices can improve the thermal comfort in indoor environment, and also reduce cooling and heating energy consumption in dry and hot climate.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 165-180
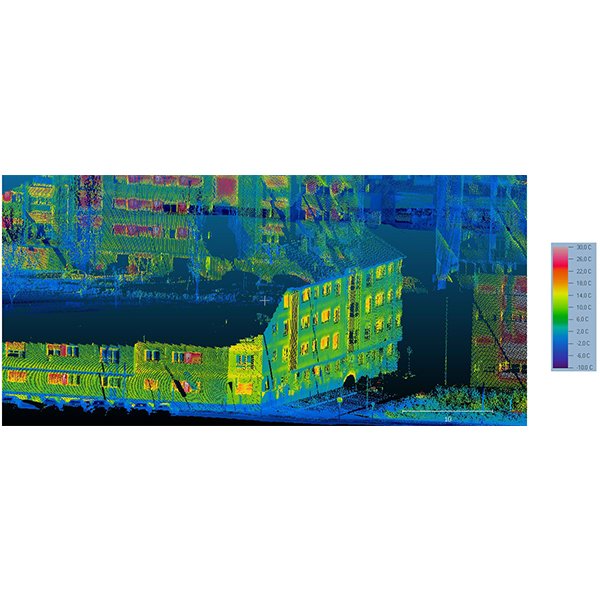
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Thermographic Mobile Mapping of Urban Environment for Lighting and Energy
The generation of 3D models of buildings has been proved as a useful procedure for multiple applications related to energy, from energy rehabilitation management to design of heating systems, analysis of solar contribution to both heating and lighting of buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 8-15

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Application of Micro-structured Sunlighting Systems in Different Climatic Zones
Two-sided micro-structures on windowpanes have been developed for redirecting sunlight into the depth of rooms in order to improve daylighting. In a joint research project comprehensive sunlighting-systems for windows are developed, integrating micro-structures in triple-glass units.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 52-59

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design of a Multi-Surface Solar Concentrator
A multi-surface solar concentrator is proposed in this study. The concentrator is designed by improving the light receiving rate of a parabola when the incident angle changes within 0°~20° by adding involute, shifting the involute up, and changing the shape of the parabolic top. .
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 176-186
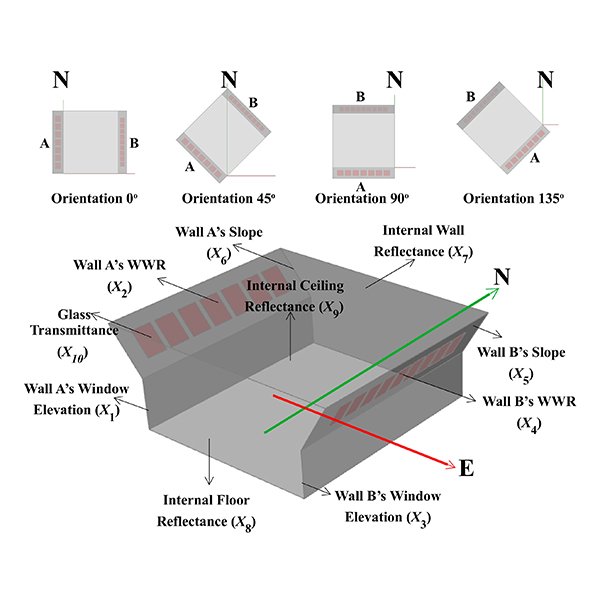
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimization of Daylighting Design Using Self-Shading Mechanism in Tropical
Despite its potential, daylighting strategies in school classrooms in the tropical climate regions is little explored in the literature. The use of two-sided or bilateral daylight opening, as well as the self-shading mechanism using sloped walls, are currently seen as potential strategies to achieve good daylighting in tropical buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 117-136

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylight utilization with light pipe in farm animal production: a
Light pipes, which are complex optical systems, offer a passive way to bring daylight to deep buildings, such as agricultural buildings. However, the lack of reliable performance predictability methods for light pipes represents a major obstacle preventing their widespread use.
Journal of Daylighting 3 (2016) 1-11
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluation of the Visual Comfort and Daylight Performance of the
The daylight in classrooms is a crucial aspect that affects the quality of the learning environment and the overall performance of the students. Visual arts, such as painting, sculpture, carving, textile design and photography, require specific lighting conditions, which are different from the regular classroom standards.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 117-135

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimization of Daylight Performance Based on Controllable Light-shelf Parameters
This study aims to achieve a balance of daylight availability in the work-plane environments of a fully glazed facade integrated with a light shelf system using an optimization procedure that can assist architects with assessing the daylighting performance of numerous design alternatives, and build-up the optimized design.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 122-136

RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Novel Approach to Multi-Apertures and Multi-Aspects Ratio
Daylightophil architecture concept is one of the most significant ways to reduce the electrical load consumption in building sector. In deep-plan buildings, or windowless buildings, advanced light transmission systems are used to compensate lighting demands in high-performance architecture theory.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 186-200
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Experimental Investigation of Overall Energy Performance in Algerian Office Building
Building integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) energy has now become one of the most significant renewable energy alternatives for providing natural daylight and clean energy.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 23-41

RESEARCH ARTICLE
An Investigation-Based Optimization Framework of Thermal Comfort Analysis in
Optimization becomes more valuable when the optimal variables decision can consider sensitivity analysis. To get optimum results quickly, this study established a synthetic sensitivity analysis and multi-objective optimization approach, which is combined with an energy simulation framework characterized by parallel processing.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 48-63

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Development of Fresnel-based Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV) System with Uniform
Different designs have been presented to achieve high concentration and uniformity for the concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) system. Most of the designs have issues of low efficiency in terms of irradiance uniformity.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 2-7

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimal Window to Wall Ratio Ranges of Photovoltachromic Windows in
Windows are one of the weakest building components concerning high thermal losses. Traditional windows cannot adapt to external and internal environmental conditions.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 134-148

REVIEW ARTICLE
Daylight Transport Systems for Buildings at High Latitudes
This paper is a literature study of daylight transport systems aiming at selecting the most appropriate ones for application at high latitudes. It is limited to the systems that transport light at a long distance from the façade and distribute it either in the building core or at a rear place in a room adjacent to the façade. .
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 60-79
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylighting metrics: an approach to dynamic cubic illuminance
Advances in research work in the field of numerical analysis of daylight performance have generated in-depth knowledge on photometric measurements of daylight quality.
Journal of Daylighting 5 (2018) 34-42
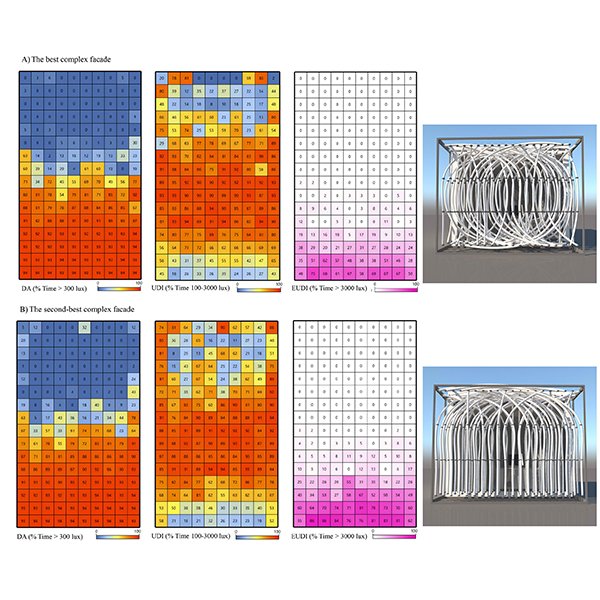
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Biomimetic Kinetic Shading Facade Inspired by Tree Morphology for Improving
Many recent studies in the field of the kinetic façade developed the grid-based modular forms through primary kinetic movements which are restricted in the simple shapes..
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 65-85

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylighting Performance of Integrated Light Shelf with Horizontal Light Pipe
Tropical countries such as Malaysia receives a significant amount of daylight. The utilisation of this renewable resource in a high-rise office building leads to opportunities and challenges.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 83-96
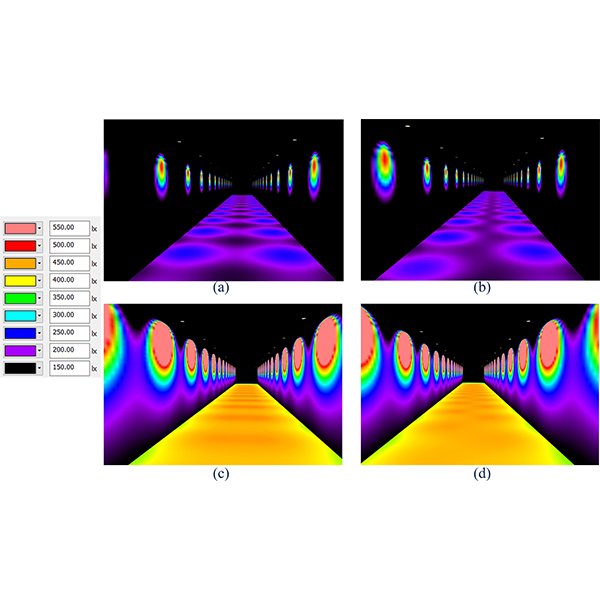
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Phasor Method to Estimate Illuminances Due to Parallel Arrays of
Direct horizontal illuminance along a calculation row due to two parallel arrays of large numbers of identical light sources behaves like a periodic signal with a sinusoidal pattern, which contains useful information for design purpose.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 246-257
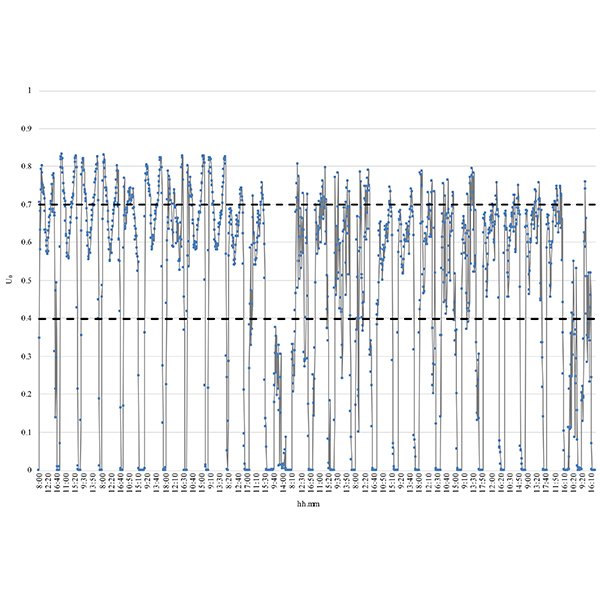
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Experimental Analysis on a 1:2 Scale Model of the
This paper is focused on the daylighting system named Modified Double Light Pipe (MDLP) designed by the authors as an evolution of the Double Light Pipe to eliminate the drawbacks due to its encumbrance and the high luminance of its upper portion.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 228-241
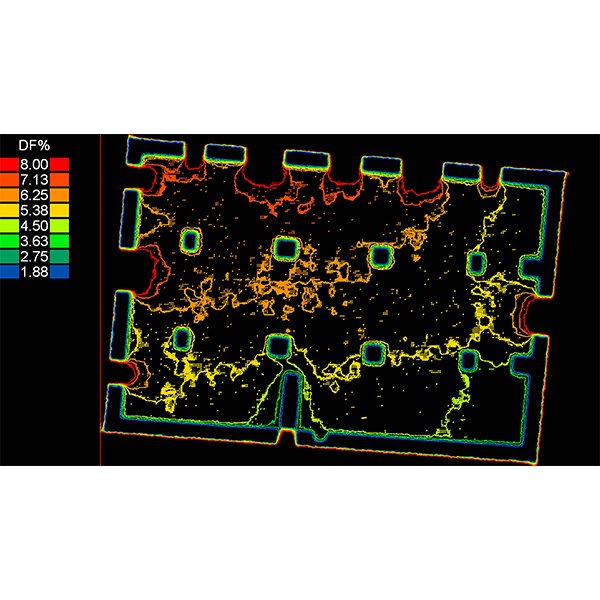
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Analysing the Daylighting Performance of the Main Prayer-hall in
This paper studies the daylighting quality of the indoor prayer-hall in The Great Upper Mosque of Hama city in Syria, highlighting this distinctive historical converted building that has been functioning as a mosque since the entry of Islam in the 6th century AD.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 153-172

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Impact of Window Design on Dynamic Daylight Performance in an
Window design affects the building's appearance. Besides, it has a significant impact on daylight performance and the visual comfort of interior spaces.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 31-44
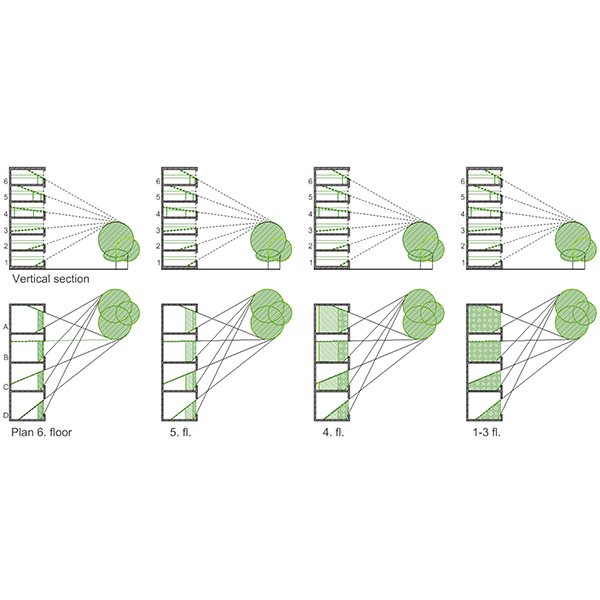
SHORT COMMUNICATION
No-Greenery Line and Greenery-View Factor, New Architectural Design
The paper proposes a new tool for evaluation of the degree of visual contact with the outdoor greenery, the Greenery-View factor (GV), intended to be easy to grasp and simple to use.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 282-286

RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Impact of Courtyard and Street Canyon Surroundings on Global
Exposing oneself to outdoor daylight in the morning can be healthy and harmful at the same time, due to the risk of ultraviolet exposure. The presence of surrounding buildings in the urban context may also influence the risk.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 167-185
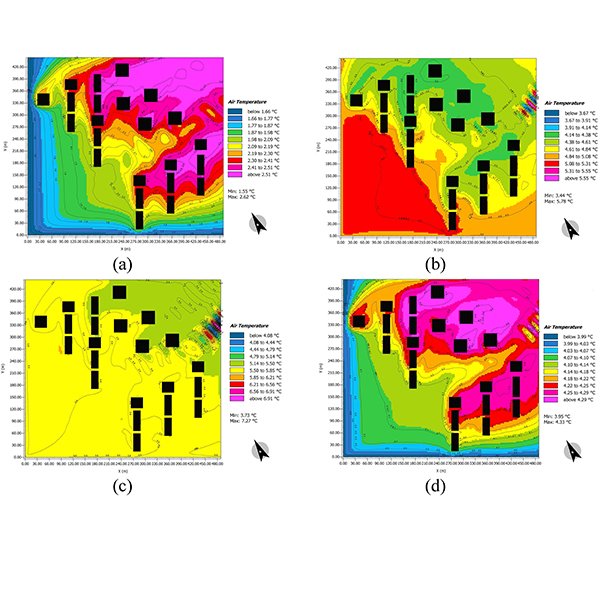
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Effect of Sky View Factor on Air temperature in
Urban geometry is defined by the height, length, width, and distance of buildings, which affect the urban environment and its microclimate, especially a high-rise and high-density urban environment, such as Tehran.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 42-51
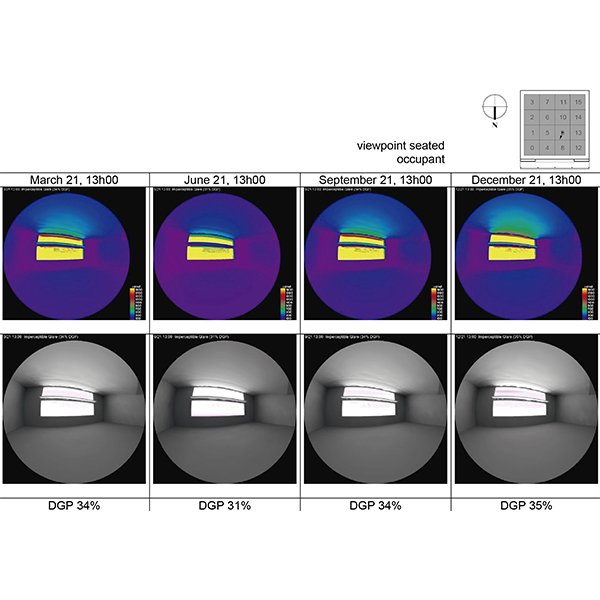
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimisation of Passive Solar Design Strategies in Side-lit Offices:
It has been shown that in buildings with fully glazed facades designed to save electricity and increase daylight, overheating due to excessive solar gains and glare have become recurrent problems, affecting the quality of the indoor environment in office buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 107-121

RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Methodology to Link the Internal Heat Gains from Lighting
This paper critically discusses the procedure prescribed by the Italian Technical Standards to account for the internal gains in the calculation of the energy performance indices for a building.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 56-67
 HOME
HOME