Journal of Daylighting
Journal of Daylighting is a peer-reviewed international journal devoted to investigations of daylighting in buildings. It is the leading journal that publishes original research on all aspects of solar energy, buildings, and lighting. Read more
Open Access — free for readers, articles are published free-of-cost.
Rapid Publication: Bi-annual (articles are published continuously throughout the year)
Publication Fee: No charges
Year Started: 2014
Time to Publication: 70 days
Abstracting & Indexing
Scopus (Elsevier)
EBSCO
Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ)
Architectural Periodicals Avery Index
CrossRef
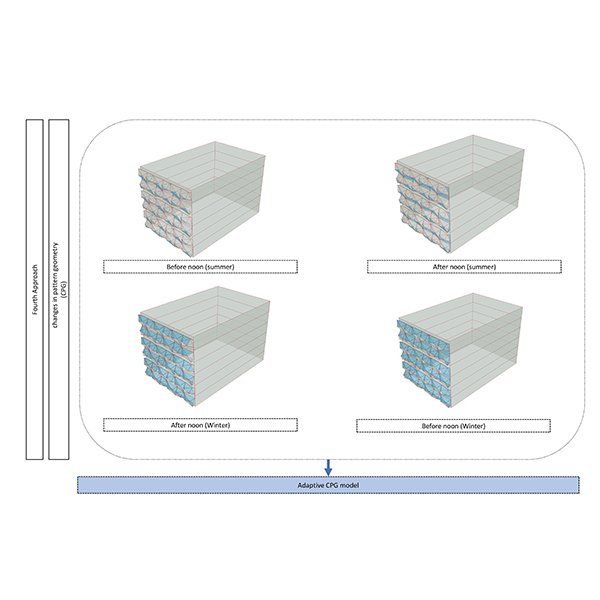
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Synergistic Strategies: Comparing Energy Performance in Climate-Adaptive Building Envelopes
Climate change and improving building energy performance are significant contemporary concerns. Conversely, climate-adaptive building envelopes (CABEs) offer promising solutions to enhance structural performance amidst fluctuating environmental conditions.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 181-202
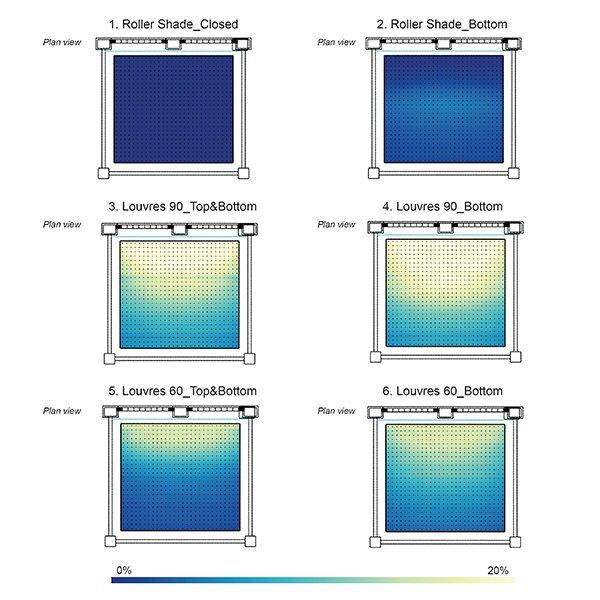
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design Adjustments For Daylighting and Visual Comfort in a Classroom
This paper evaluates how design adjustments applied to roller shades and louvres (namely the height of the shadings head and the angles of the louvre slats) can improve their annual and spatial effectiveness to provide autonomous daylight levels, reduce daylight glare problems, and offer views outside.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 165-180
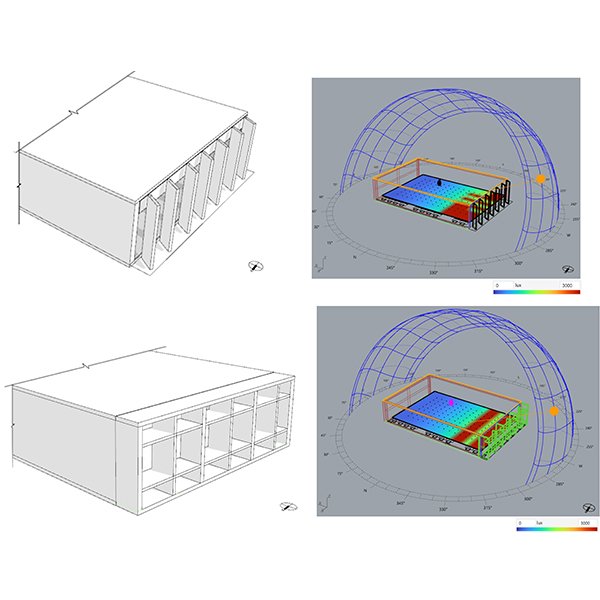
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Performance of Shading Against West Glass Facades to Optimise Daylight,
In tropical urban areas, the vertical facades of buildings often play a crucial role in capturing solar radiation and heat, especially for office buildings facing west during the afternoon.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 131-148
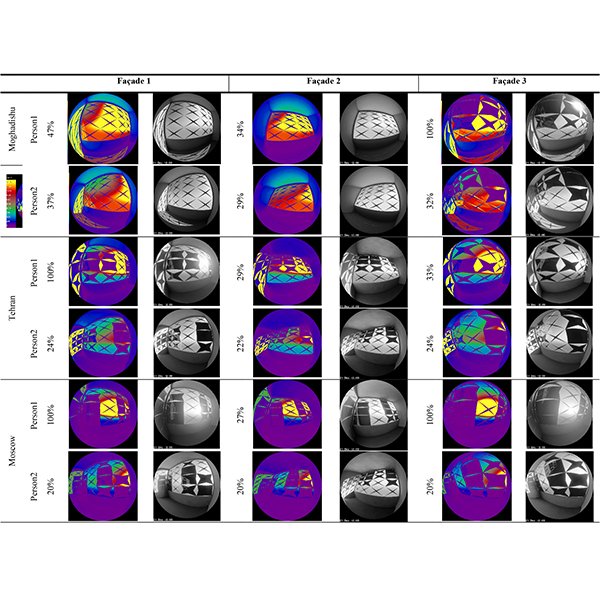
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Designerly Approach to Design Responsive Façade for Occupant Visual
In recent years, attention has focused on improving the health and satisfaction of employees by enhancing visual comfort in workplaces. This involves providing adequate natural daylight, glare control, and outdoor views.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 149-164
RESEARCH ARTICLE
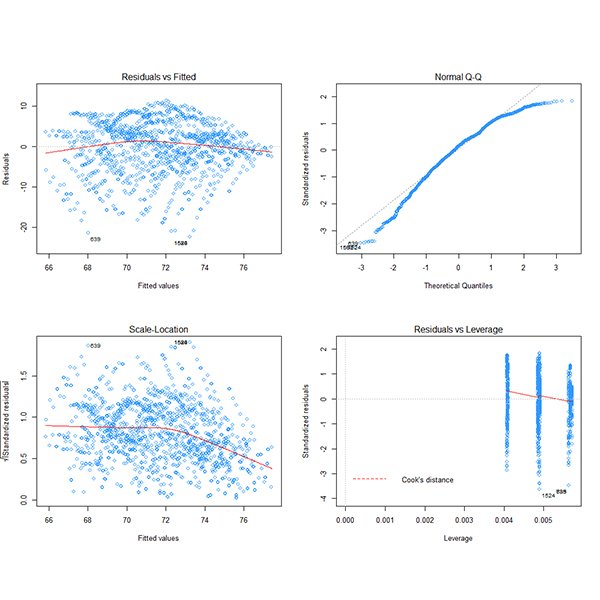
Geometry Optimization of Industry Buildings for Energy-Driven Design Development
Even though the manufacturing industry consumes roughly 54% of total available energy globally, little consideration has been devoted to optimizing energy in the early stages of industry design, particularly in densely populated cities.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 119-130
REVIEW ARTICLE
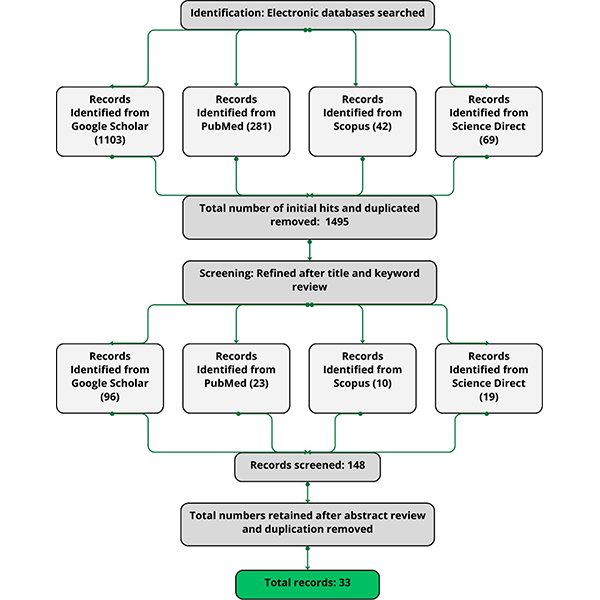
Exploring Methodological Considerations: A Literature Review on How Lighting Affects
The impacts of lighting conditions on human circadian rhythms, sleep quality, and cognitive performance have been extensively investigated in the past two decades; however, these studies have yielded inconclusive and variable outcomes.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 97-118

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Enhancing Visual Comfort and Energy Efficiency in Office Lighting Using
The number of desk workers who frequently conduct their jobs at home has increased dramatically during Covid-19. Work-from-home flexibility makes it attractive for workers and companies, resulting in a “Work-Style Reform” after the Covid-19 pandemic. Ho.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 69-96
RESEARCH ARTICLE
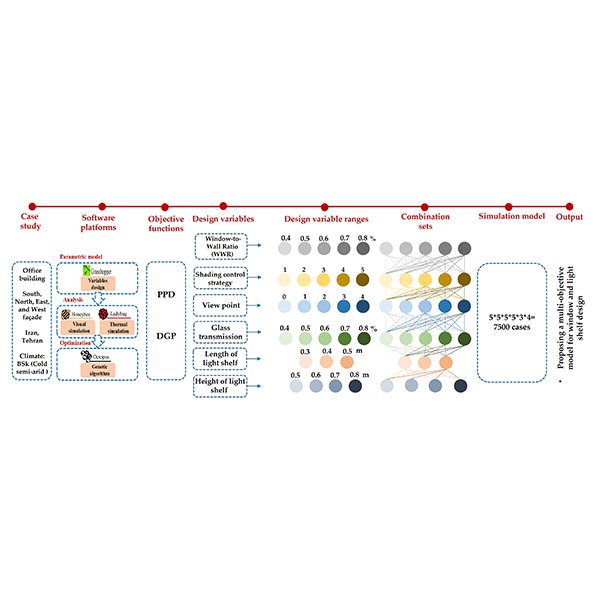
A Multi-objective Optimization of Window and Light Shelf Design
In office buildings, an efficient design of windows and using light shelves as a passive design strategy significantly influence the thermal and visual comfort of occupants while enhancing the productivity and health of users.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 55-68
RESEARCH ARTICLE
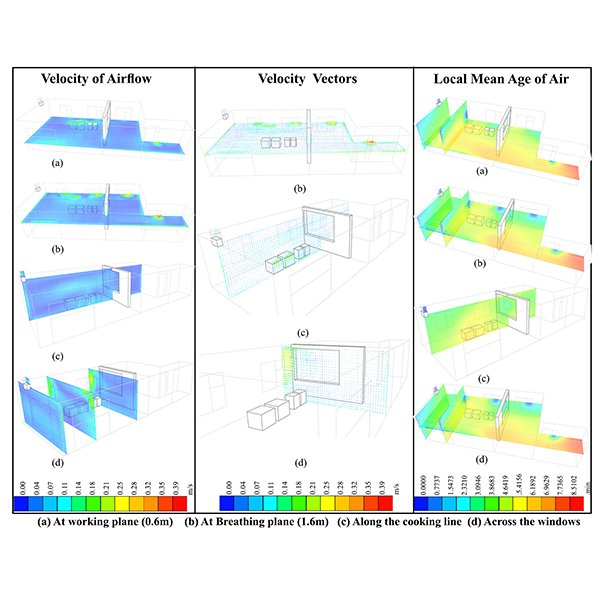
Investigation of Ventilation Performance to Improve the Indoor Air Quality
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) is a significant health determinant in the building environment. Ventilation plays a significant role in providing comfortable working conditions and securing contaminant removal from indoor spaces.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 39-54
RESEARCH ARTICLE
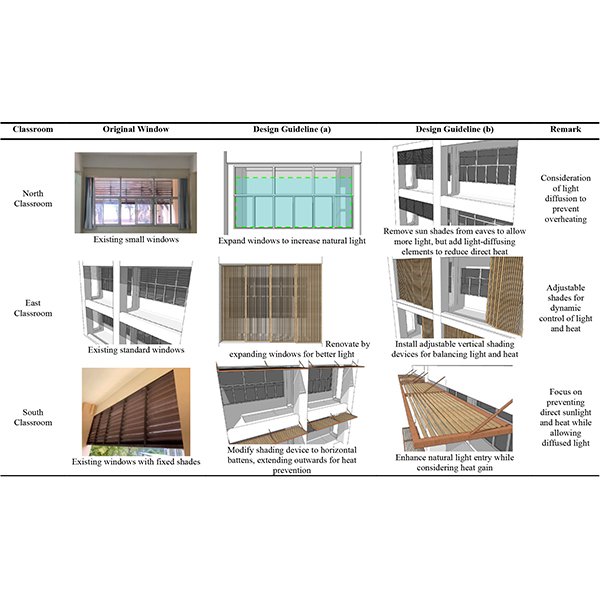
Improving Natural and Artificial Lighting in Coastal Architecture Classrooms: Insights
This research examines the natural and artificial lighting performance comparison in an architecture classroom at a university in southern Thailand and gives principles for enhancing lighting design.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 23-38

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Electrochromic Glazing and Evaluation of Visual and Non-Visual Effects
The employment of electrochromic glazing can be a solution to balance circadian lighting and avoid glare. This can be achieved by controlling daylight entering the room and may be useful within the context of highly glazed facades in buildings in hot climates.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 1-22
RESEARCH ARTICLE
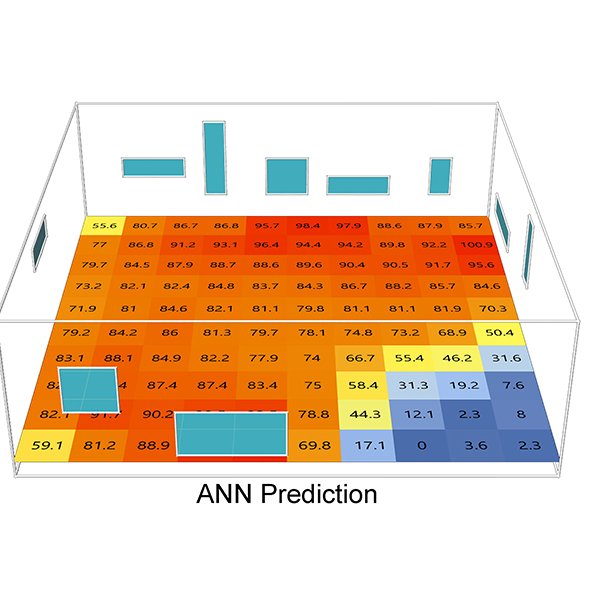
Unfolding 3D Space into Binary Images for Daylight Simulation via
Daylighting plays a crucial role in building science, impacting both occupants’ well-being and energy consumption in buildings. Balancing the size of openings with energy efficiency has long been a challenge. .
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 204-2013
RESEARCH ARTICLE
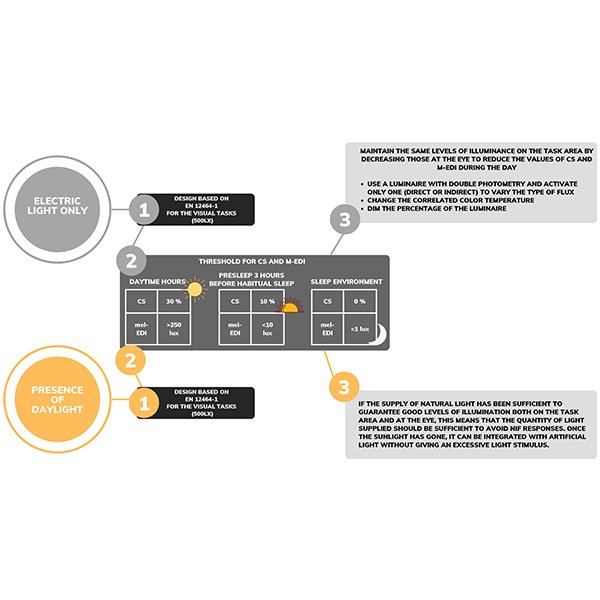
Integrative Lighting Design: How to Optimize Visual and Non-visual
The objective of this paper is to outline fundamental principles for the electric lighting design of workplace environments such as offices. The study considers both the suggested guidelines and values for non-visual light design and the specifications for visual tasks dictated by the EN 12464-1:2021.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 192-203
RESEARCH ARTICLE
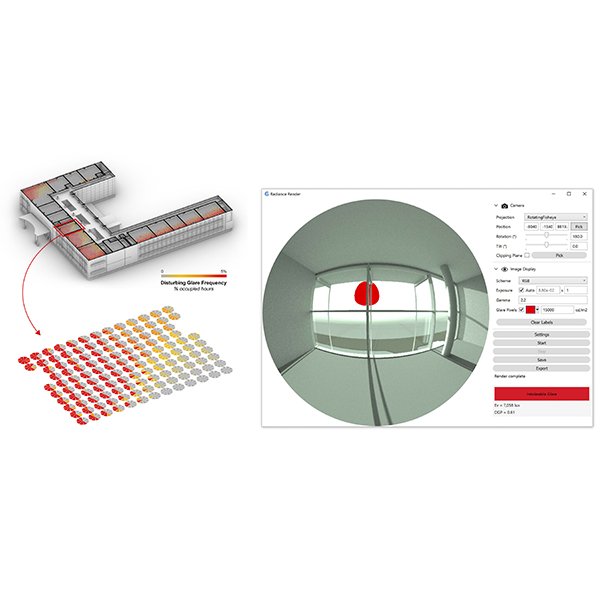
The Effect of Parametric Patterned Façade Variations on Daylight
Parametric design influences on building envelope design are exponentially increasing in the current era due to the dominance of computational design on architectural outcomes.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 173-191
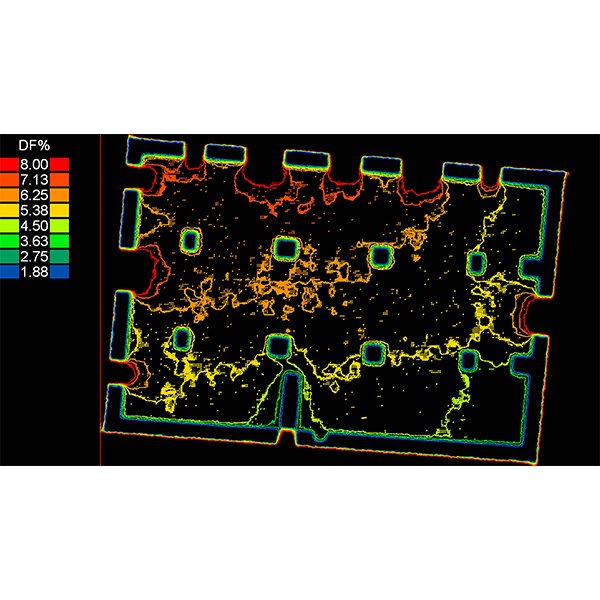
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Analysing the Daylighting Performance of the Main Prayer-hall in
This paper studies the daylighting quality of the indoor prayer-hall in The Great Upper Mosque of Hama city in Syria, highlighting this distinctive historical converted building that has been functioning as a mosque since the entry of Islam in the 6th century AD.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 153-172
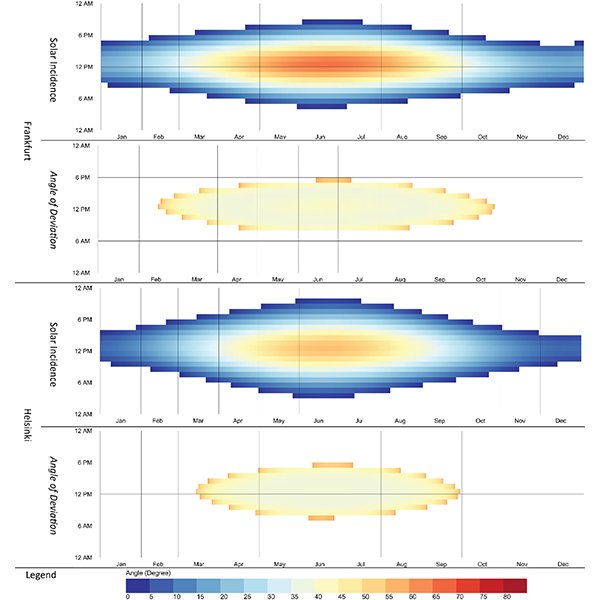
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Solar Angle Model for Daylight Redirection in Prismatic Panel
An advanced complex fenestration system can utilize uniform daylight. Nonetheless, an inefficient design would increase solar heat gain and indoor temperatures, besides uneven light distribution that would cause the "cave effect.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 257-265
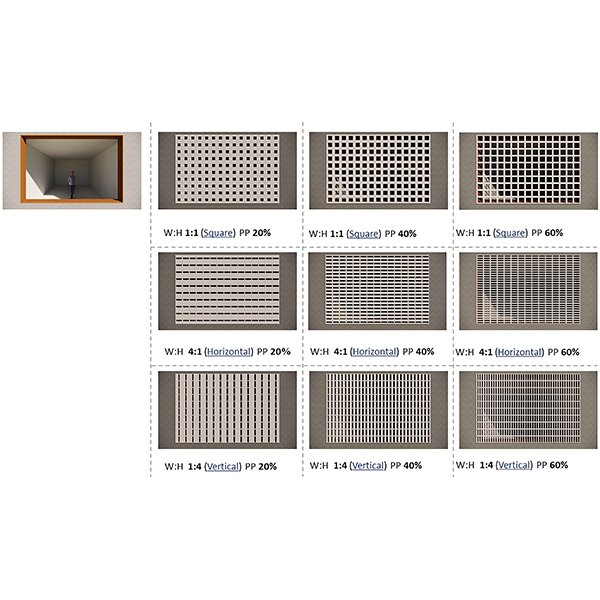
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Significance of Aperture Proportion for the Lighting Behaviour and
Traditional solar screens in Iran (called Moshabak) are architectural devices used mainly in hot-arid regions, with two interrelated functions: controlling the penetration of sunlight and gaze from outside.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 242-256
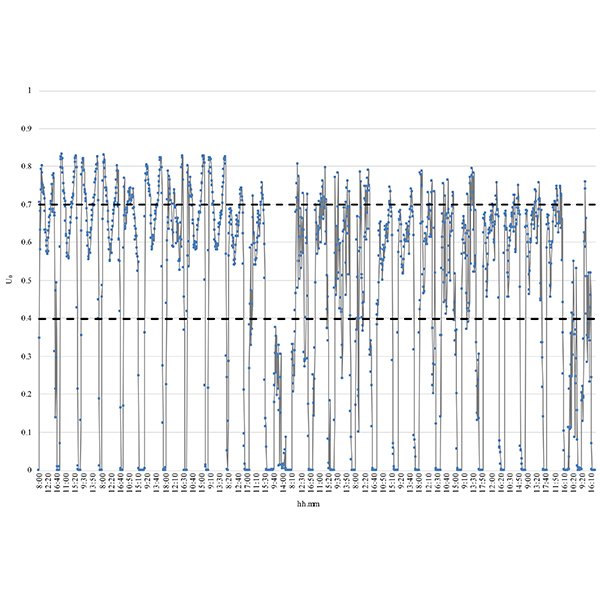
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Experimental Analysis on a 1:2 Scale Model of the
This paper is focused on the daylighting system named Modified Double Light Pipe (MDLP) designed by the authors as an evolution of the Double Light Pipe to eliminate the drawbacks due to its encumbrance and the high luminance of its upper portion.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 228-241
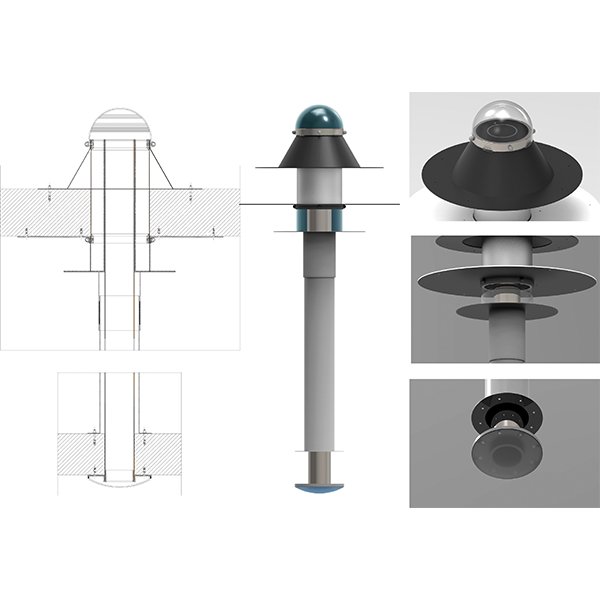
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Illumination and Lighting Energy Use in an Office Room with
This paper describes a field study of the illumination and lighting energy use in a full-scale test office in a building located in southern Norway. Natural light is provided to the office via southwest-oriented windows and a horizontal light pipe (HLP) with a daylight entrance facing the south.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 209-227
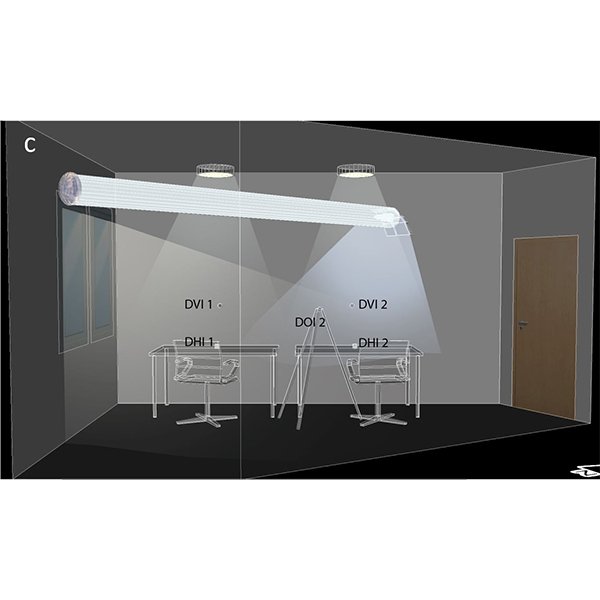
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluation of Daylight and Glare Quality of Office Spaces with
There has been an increasing awareness in recent years about the evaluation of daylight and glare quality in buildings. In the study, an office space with a flat and a dynamic shading system facade (triangular cell facade) is discussed in the province of Mardin, which is in a hot and arid climate zone.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 197-208
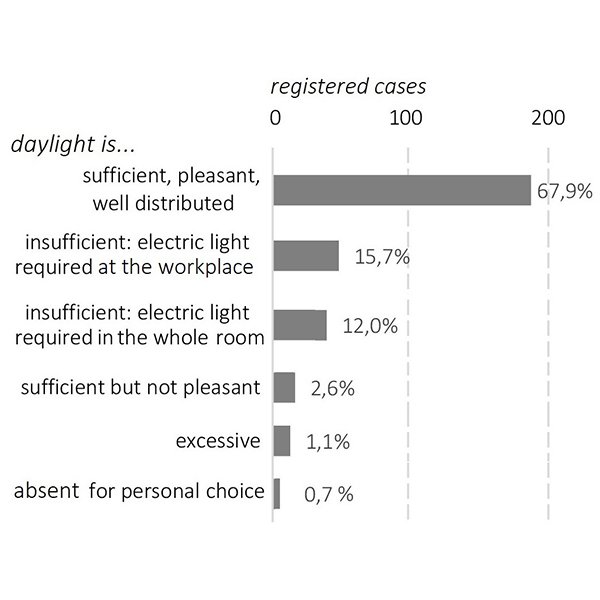
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Lighting Quality Self-assessment in Italian Home Offices
The spread of information technology and the improvement of telecommunicating systems have changed the way to conceive work. People performing typical office activities provided with a laptop and an internet connection can work in whatever place: a coffee house, a waiting room of a train station, an airport, or their own home.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 177-196
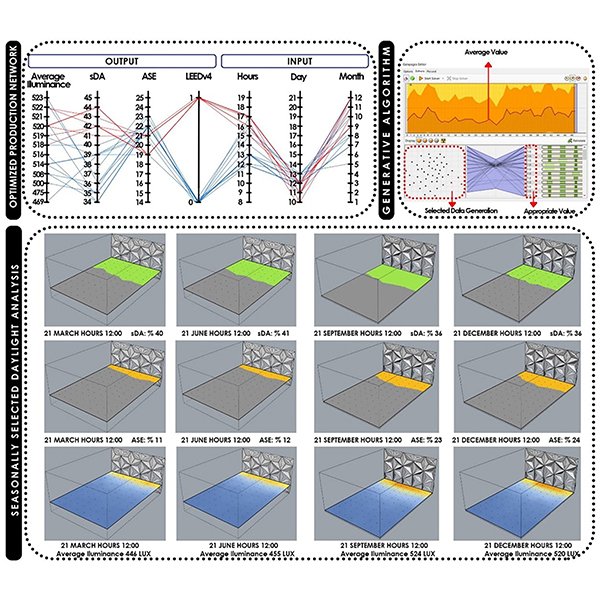
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylight Performance of the Modified Double Light Pipe (MDLP) Through
This paper focuses on the Modified Double Light Pipe (MDLP), an innovative daylighting system set up by the authors in the Laboratory of Technical Physics of the University “G. .
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 164-176
REVIEW ARTICLE
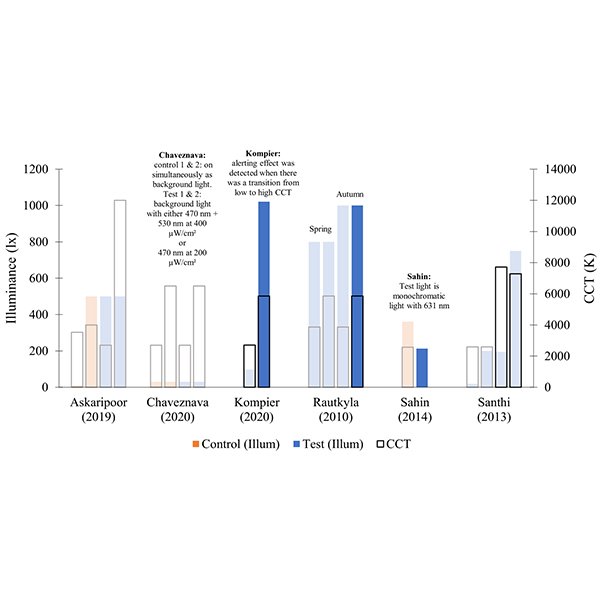
Alerting Effect of Light: A Review of Daytime Studies
Light affects humans beyond only image formation. Several studies have reported that light can increase daytime alertness and can therefore be positively utilized to counter daytime fatigue and increase productivity in workspaces.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 150-163
RESEARCH ARTICLE
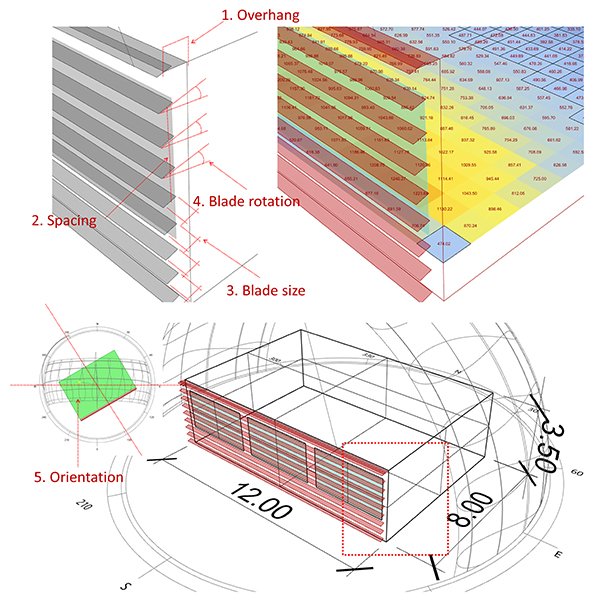
The optimization of louvers shading devices and room orientation under
This paper presents parametric and multi-objective optimization (MOO) approach in optimizing daylight and energy consumption by incorporating louvres shading devices depicting three different sky conditions: Birmingham, UK, Jakarta, Indonesia, and Sydney, Australia.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 137-149
RESEARCH ARTICLE
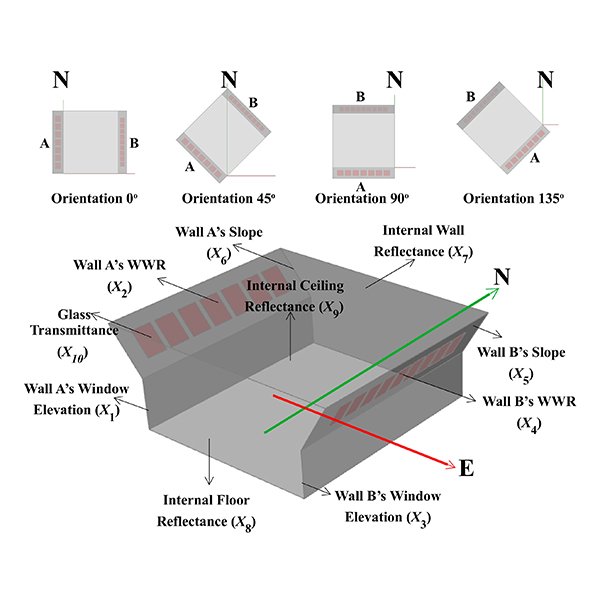
Optimization of Daylighting Design Using Self-Shading Mechanism in Tropical
Despite its potential, daylighting strategies in school classrooms in the tropical climate regions is little explored in the literature. The use of two-sided or bilateral daylight opening, as well as the self-shading mechanism using sloped walls, are currently seen as potential strategies to achieve good daylighting in tropical buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 117-136
RESEARCH ARTICLE
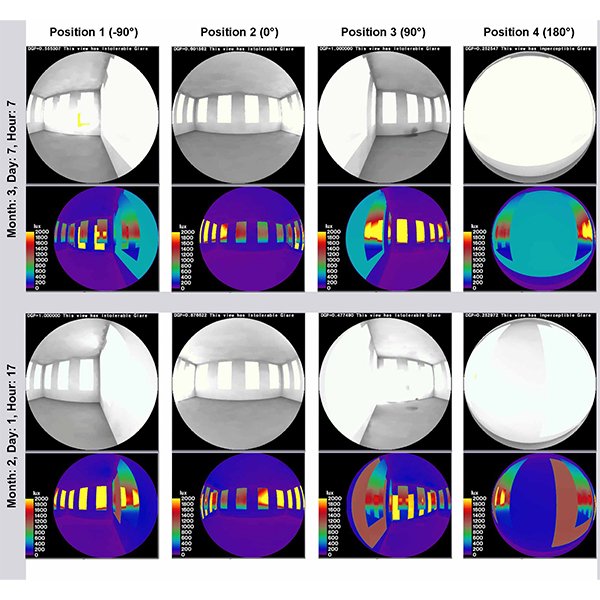
Impact of Different Shading Devices on Daylight Performance and Visual
Daylighting has become an essential feature in libraries since it can boost productivity, well-being, and energy savings. It is crucial to prevent discomfort glare irritation while maintaining the quality of view, and daylight demands.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 97-116

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylighting Performance of Integrated Light Shelf with Horizontal Light Pipe
Tropical countries such as Malaysia receives a significant amount of daylight. The utilisation of this renewable resource in a high-rise office building leads to opportunities and challenges.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 83-96
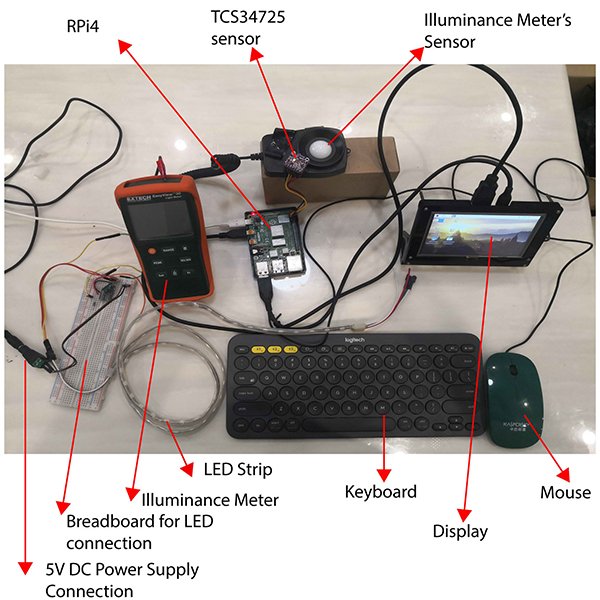
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design and Simulation of a Circadian Lighting Control System Using
This paper introduces a fuzzy logic-based circadian lighting control system using flexibility of Light-Emitting Diode (LED) lighting technology to synchronise artificial lighting with circadian (natural) lighting Correlated Colour Temperature (CCT) characteristics.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 64-82

RESEARCH ARTICLE
An Investigation-Based Optimization Framework of Thermal Comfort Analysis in
Optimization becomes more valuable when the optimal variables decision can consider sensitivity analysis. To get optimum results quickly, this study established a synthetic sensitivity analysis and multi-objective optimization approach, which is combined with an energy simulation framework characterized by parallel processing.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 48-63
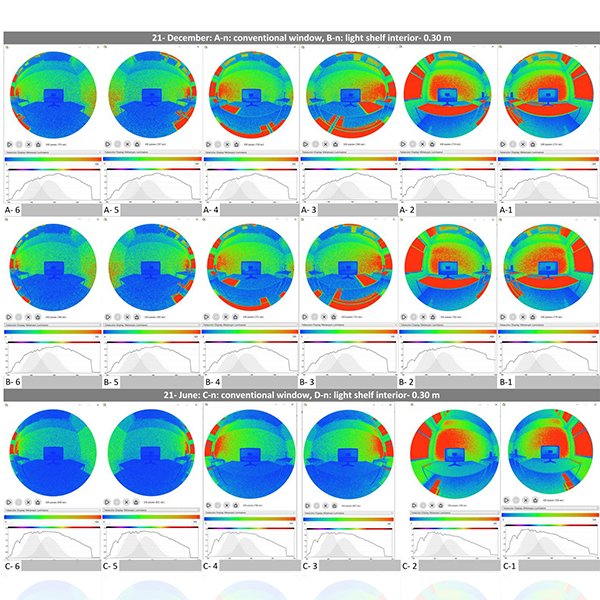
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Daylight Assessment on Visual and Nonvisual Effects of Light
The contribution of daylight to a comfortable environment for occupants has been the subject of studies for years. Light shelves are known as daylight redirecting systems to enhance indoor daylight conditions.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 28-47
Rank
Energy (miscellaneous): #36/78
Renewable Energy, Sustainability and the Environment: #140/270
CiteScoreTM 2023: 4.0
Editorial Board

Dr Susana Lagüela López
University of Vigo, Spain

Dr Arsenio Barbón
University of Oviedo, Spain

Prof. Barbara Szybinska Matusiak
NTNU, Norway

Dr Valerio Roberto Maria Lo Verso
Politecnico di Torino (Polytechnic University of Turin), Italy

Prof Hongfei Zheng
Beijing Institute of Technology, China

Dr Umberto Berardi
Ryerson University, canada

Prof. Yuehong Su
University of Nottingham, UK

Prof Francesco Asdrubali
University of Perugia, Italy

Prof Laura Bellia
University of Naples Federico II, Italy

Prof. Önder Güler
Istanbul Technical University, Türkiye

Dr Boon Han Lim
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Malaysia

Prof. Antonio Manuel Peña García
University of Granada, Spain

Prof. Lambros T. Doulos
Hellenic Open University, Greece

Dr Canan Kandilli
Usak University, Turkey

Dr Fabio Peron
IUAV University of Venice, Italy

Dr Marina Bonomolo
University of Palermo, Italia

Dr Doris Abigail Chi Pool
Universidad de las Américas Puebla, Mexico

Dr jian yao
Ningbo University, China

Dr Mohammed Salah Mayhoub
Al-Azhar University, Egypt

Alp Tural
Virginia Tech, USA

Dr. Feride Şener Yılmaz
Istanbul Technical University, Turkey

Dr Petar Pejic
University of Niš, Serbia

Dr Hui Shen
Texas A&M University-Kingsville, USA

Dr Lim Yaik Wah
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia

Dr Karam M. Al-Obaidi
Sheffield Hallam University, UK

Dr. Michele Rocca
University of Pisa, Italia

Prof. BANU MANAV
Kadir Has University, Turkey

Dr Paula M. Esquivias
University of Granada, Spain

Dr. Francesco Nocera
Department of Civil Engineering and Architecture, University of Catania (ITALY), Italy

Wei Wang
Southeast University, 中国
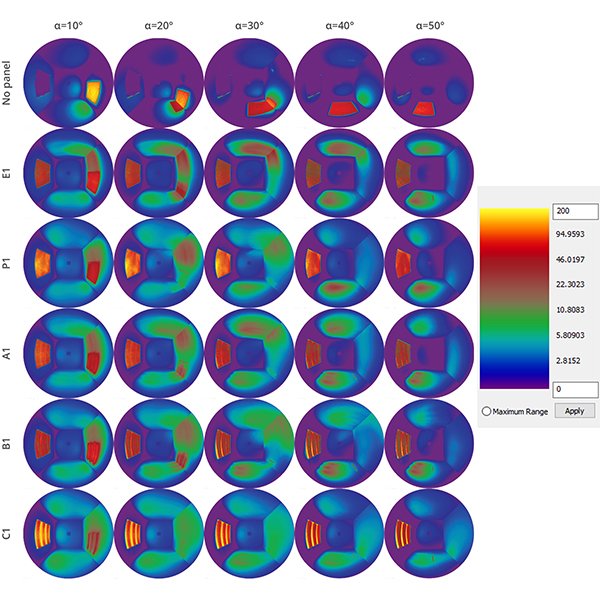
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Towards New Design of Laser Cut Acrylic Panels for Windows
This paper builds upon existing research into laser cut panels and aims to find new design-patterns that would improve daylighting conditions of existing rooms when applying the laser-cut panels on vertical windows.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 1-10

RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Methodology to Link the Internal Heat Gains from Lighting
This paper critically discusses the procedure prescribed by the Italian Technical Standards to account for the internal gains in the calculation of the energy performance indices for a building.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 56-67
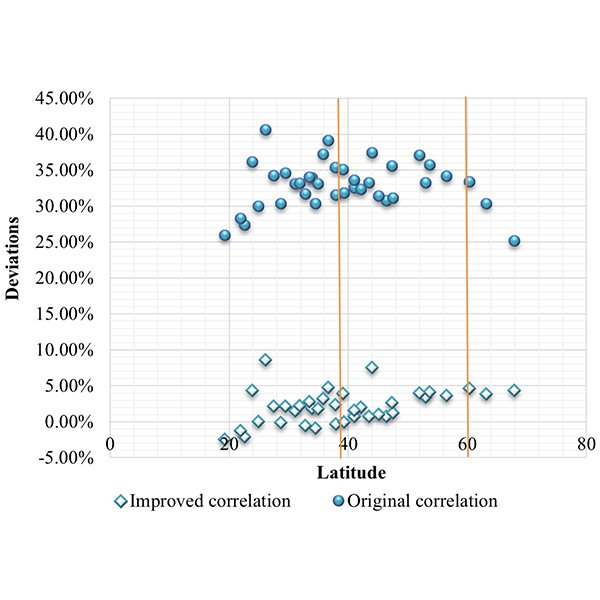
RESEARCH ARTICLE
An Improvement to Calculation of Lighting Energy Requirement in the
Daylighting has a recognized potential for electric energy savings when is used as a complement for artificial lighting. This study reviews the comprehensive calculation method for lighting energy requirement in non-residential buildings introduced by the European Standard EN 15193: 2007 and investigates its feasibility in China.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 16-28
SHORT COMMUNICATION
No-Greenery Line and Greenery-View Factor, New Architectural Design
The paper proposes a new tool for evaluation of the degree of visual contact with the outdoor greenery, the Greenery-View factor (GV), intended to be easy to grasp and simple to use.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 282-286
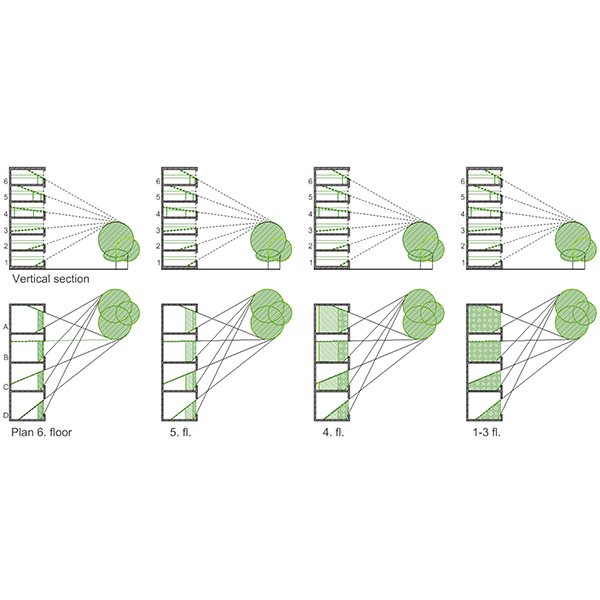
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Parametric Analysis of Architectural Elements on Daylight, Visual Comfort, and
The quality of visual comfort has always been an essential element considering human comfort. Providing visual comfort in a living environment reduces the need for artificial lighting, which subsequently has a direct relationship with energy consumptions and its expenses.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 57-72
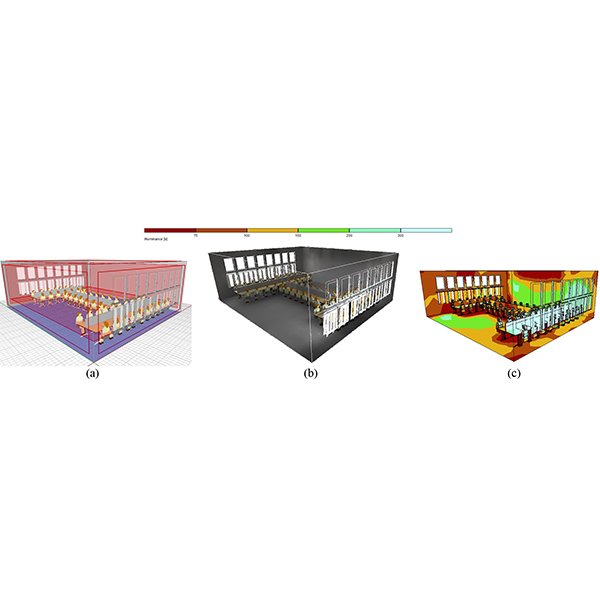
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Effect of Sky View Factor on Air temperature in
Urban geometry is defined by the height, length, width, and distance of buildings, which affect the urban environment and its microclimate, especially a high-rise and high-density urban environment, such as Tehran.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 42-51
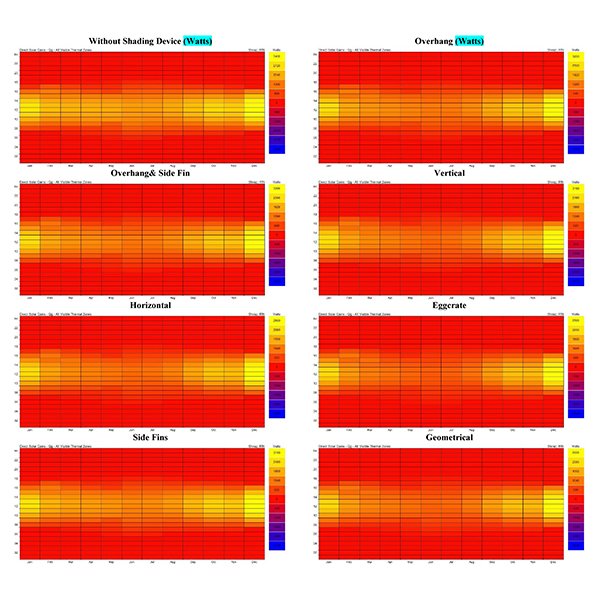
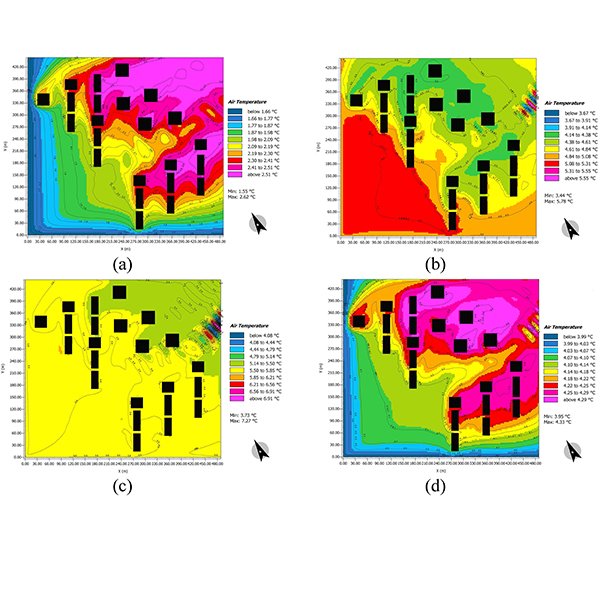
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Effect of Fixed External Shading Devices on Daylighting and
Building shading devices can improve the thermal comfort in indoor environment, and also reduce cooling and heating energy consumption in dry and hot climate.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 165-180

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Lighting Energy Saving with Light Pipe in Farm Animal Production
The Swedish animal production sector has potential for saving electric lighting of €4-9 million per year using efficient daylight utilisation. To demonstrate this, two light pipe systems, Velux® (house 1) and Solatube® (house 2), are installed in two identical pig houses to determine if the required light intensity, daylight autonomy (DA), and reduced electricity use for illumination can be achieved. In.
Journal of Daylighting 2 (2015) 21-31

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Acrylic Panels Applications as Building Materials and Daylighting Devices
Enormous studies have been conducted to enhance the daylighting utilization in buildings either by direct lighting techniques, lighting reflection systems, lighting transporting systems, or by light tracking systems.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 258-272

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Automatic vs Manual Control Strategy for Window Blinds and Ceiling
A case study to evaluate the occupants' satisfaction in relation to two different control strategies (fully automatic and manual) for blind and ceiling lights use in cell offices was carried on in Trondheim, Norway.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 112-123

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Lighting to Enhance Wayfinding for Thai Elderly Adults in Nursing
The main purpose of this study was to explore the effects of lighting and other environmental variables in terms of the colour, signage, and furnishings on the indoor wayfinding of Thai seniors in a nursing home.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 25-36
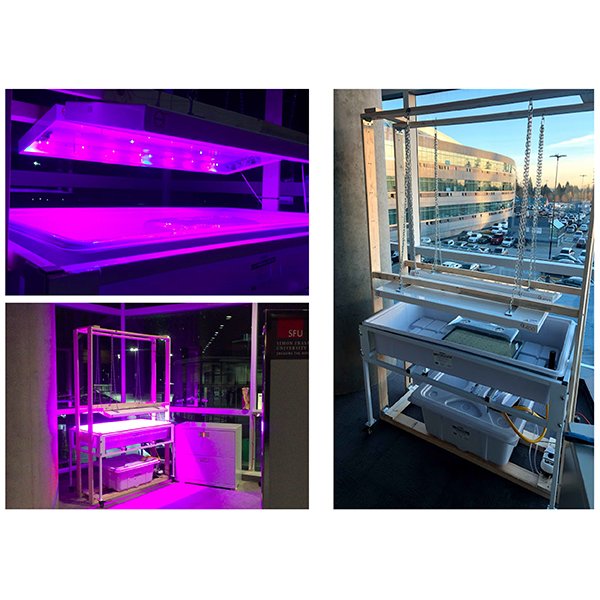

RESEARCH ARTICLE
An Intelligent IoT-enabled Lighting System for Energy-efficient Crop
In this paper, an intelligent lighting instrumentation and automation system is presented with the objective of achieving high energy-efficiency in greenhouse supplemental lighting based on the Internet of Things (IoT) technology.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 86-99
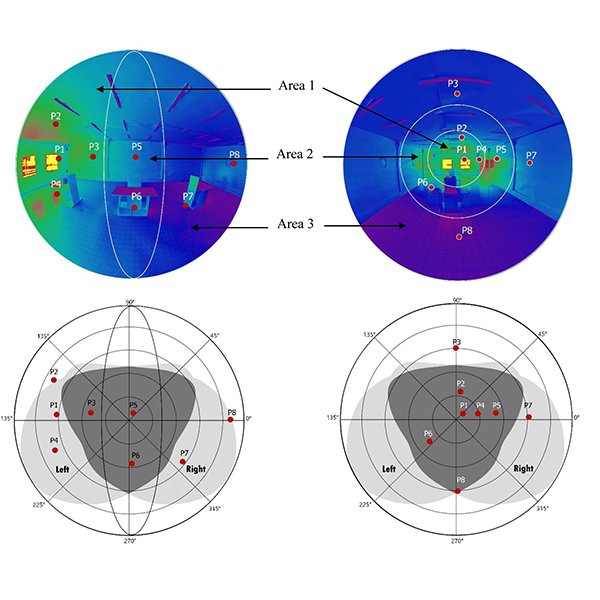
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Combined Method for an Exhaustive Investigation of the Anidolic
Lighting quality in office environments is a broad concept that must be taken into account in the design stage to deliver comfortable spaces to reduce workers' stress.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 149-164

RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Novel Approach to Multi-Apertures and Multi-Aspects Ratio
Daylightophil architecture concept is one of the most significant ways to reduce the electrical load consumption in building sector. In deep-plan buildings, or windowless buildings, advanced light transmission systems are used to compensate lighting demands in high-performance architecture theory.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 186-200
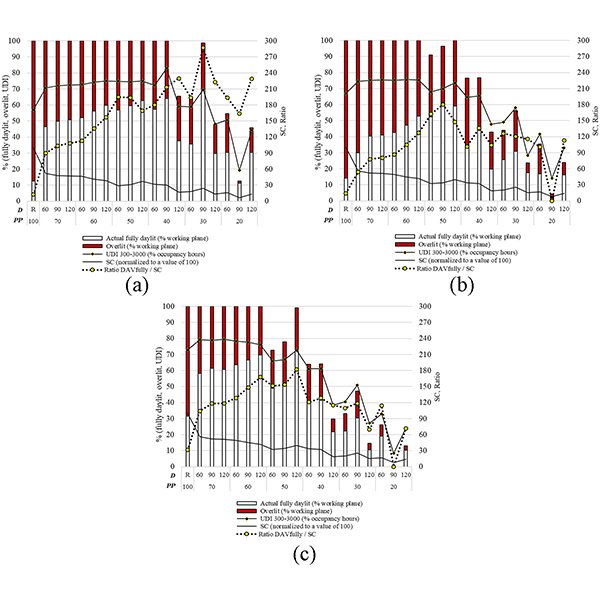
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Comprehensive Evaluation of Perforated Façades for Daylighting and
New design tools have enabled architects to explore complex geometries for building envelopes. Perforated Screens (PS) have gained popularity but their design is still intuitive, often focused on aesthetic and morphological criteria.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 97-111
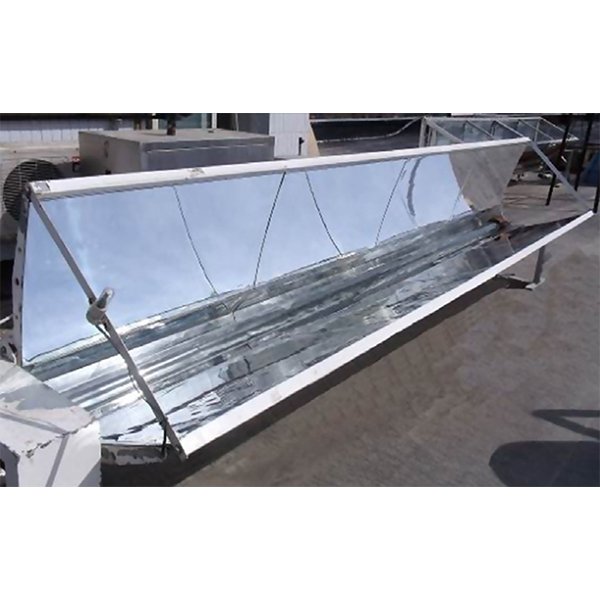

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design of a Multi-Surface Solar Concentrator
A multi-surface solar concentrator is proposed in this study. The concentrator is designed by improving the light receiving rate of a parabola when the incident angle changes within 0°~20° by adding involute, shifting the involute up, and changing the shape of the parabolic top. .
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 176-186
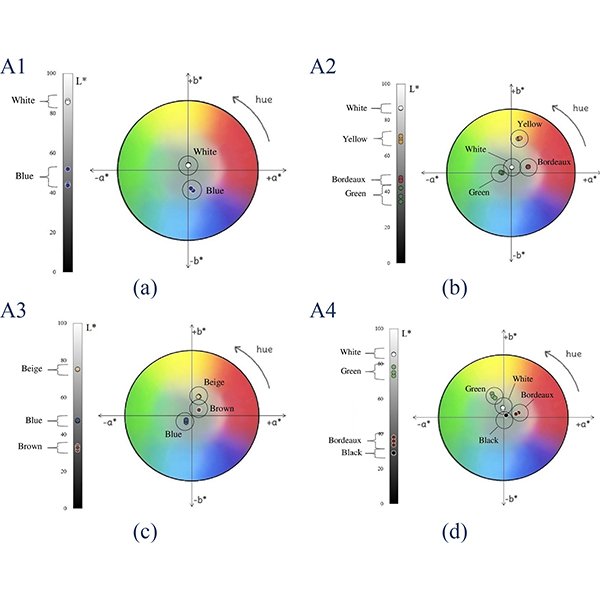
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optical Characteristics of Traditional Portuguese Azulejos: Mixing Colors to Obtain “
The need to reduce energy consumptions in buildings brings modern research to focus on the use of natural sources. In this context, the interest towards traditional architecture has been fueled, since one of the characteristics identifying it is the intuitive and intrinsic link between the building and the surrounding environment.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 273-281
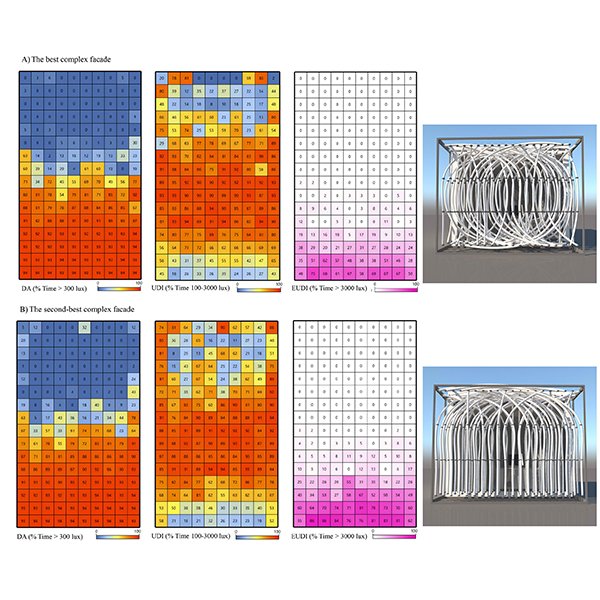
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Biomimetic Kinetic Shading Facade Inspired by Tree Morphology for Improving
Many recent studies in the field of the kinetic façade developed the grid-based modular forms through primary kinetic movements which are restricted in the simple shapes..
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 65-85

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Comparative Investigation of Daylight Glare Probability (DGP) Comfort Classes in
Glare is considered one of the most important variables to reach visual comfort and visual quality. It represents one of the fundamental barriers for an effective use of daylighting in buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 284-293
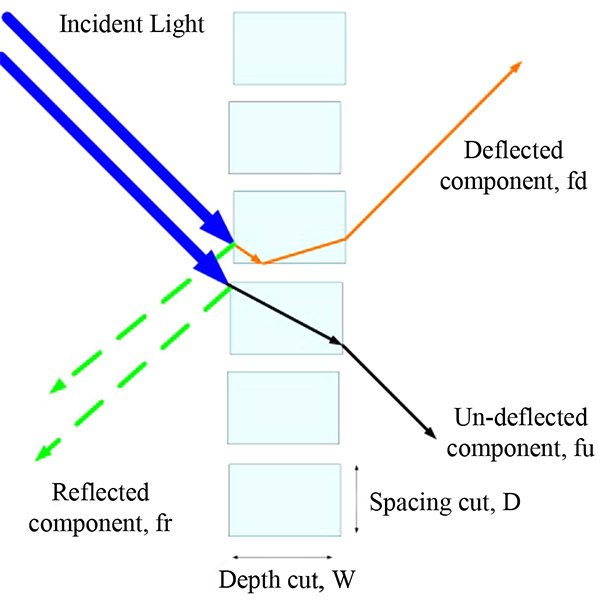
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Maximizing the Performance of Laser Cut Panel by Interaction of
The interaction between different ceiling geometries with laser cut panels (LCPs) is investigated using real experiments and computer simulations to maximize the daylight performance of the LCP.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 29-35

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylight utilization with light pipe in farm animal production: a
Light pipes, which are complex optical systems, offer a passive way to bring daylight to deep buildings, such as agricultural buildings. However, the lack of reliable performance predictability methods for light pipes represents a major obstacle preventing their widespread use.
Journal of Daylighting 3 (2016) 1-11

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Development of a Machine-Learning Framework for Overall Daylight and
Application of machine learning methods as an alternative for building simulation software has been progressive in recent years. This research is mainly focused on the assessment of machine learning algorithms in prediction of daylight and visual comfort metrics in the early design stages and providing a framework for the required analyses.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 270-283

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Measurement, Simulation, and Quantification of Lighting-Space Flicker Risk Levels
Building owners are transitioning towards a smart lighting solution for illumination purposes. LED (Light Emitting Diode) lighting application has become a norm given its high efficacy and energy efficiencies.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 239-254

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Power Factor Correction of Compact Fluorescent and Tubular LED Lamps
Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs) and Light-emitting Diode (LED) lamps have received wide acceptance in lighting applications during the last few years.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 73-83

RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Survey on Daylighting Education in Italian Universities. Knowledge of
Daylighting is a strategic topic to achieve sustainable buildings, so it is more and more imperative that it is implemented in architecture curricula to prepare a new generation of daylighting-oriented practitioners.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 36-49
 HOME
HOME