Journal of Daylighting
An international journal devoted to investigations of daylighting in buildings. It is the leading journal that publishes original research on all aspects of Energy, buildings, and lighting.
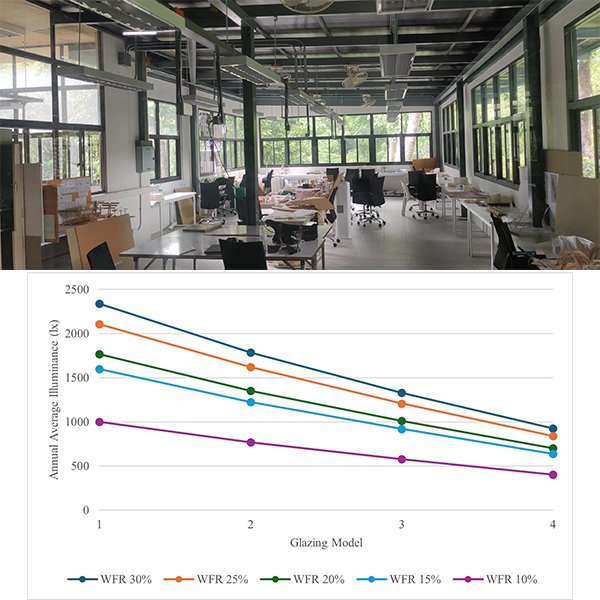
RESEARCH ARTICLE
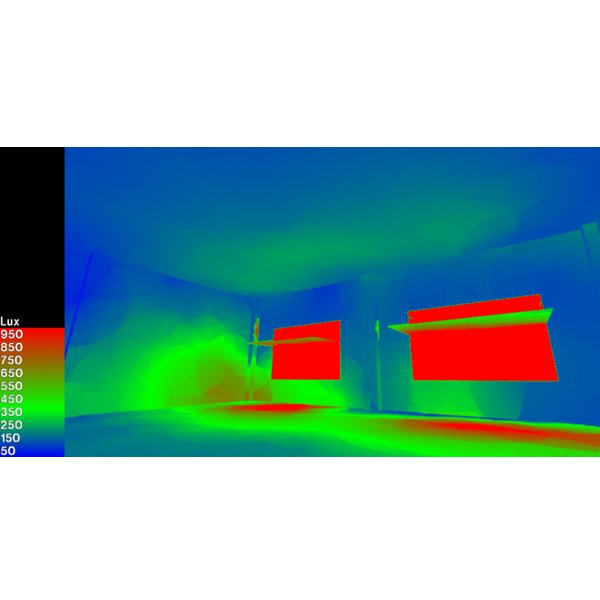
Optimizing Window-to-Floor Ratio and Glazing for Daylight and
In tropical climates, where cooling loads dominate building energy use, minimizing cooling demand is particularly critical for achieving carbon neutrality in educational buildings while maintaining adequate daylight and visual comfort.
Journal of Daylighting 13 (2026) 44-56
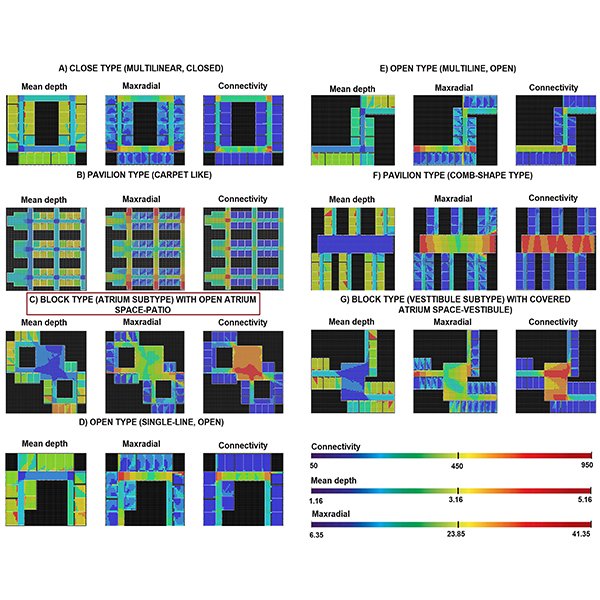
RESEARCH ARTICLE
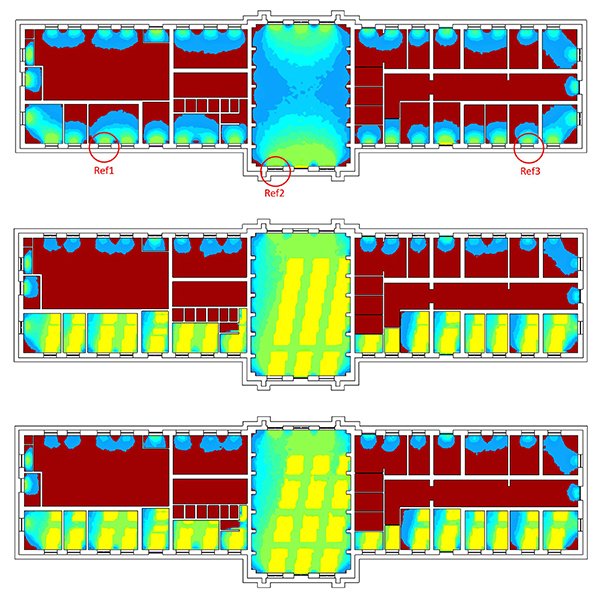
Comparative Analysis of Daylight and Visual Quality Across School Plan
Designing daylight-based spaces has gained increasing attention due to its numerous benefits and alignment with global sustainability standards. However, limited research has focused on how architectural layouts affect daylight distribution and visual quality, particularly in educational environments.
Journal of Daylighting 13 (2026) 20-43
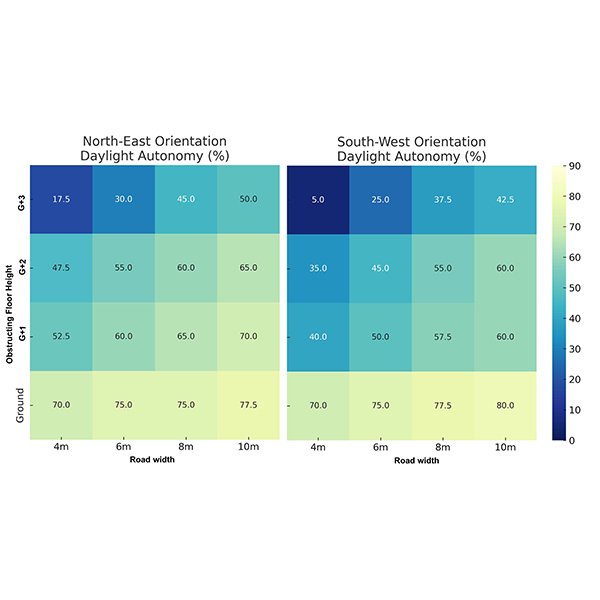
RESEARCH ARTICLE
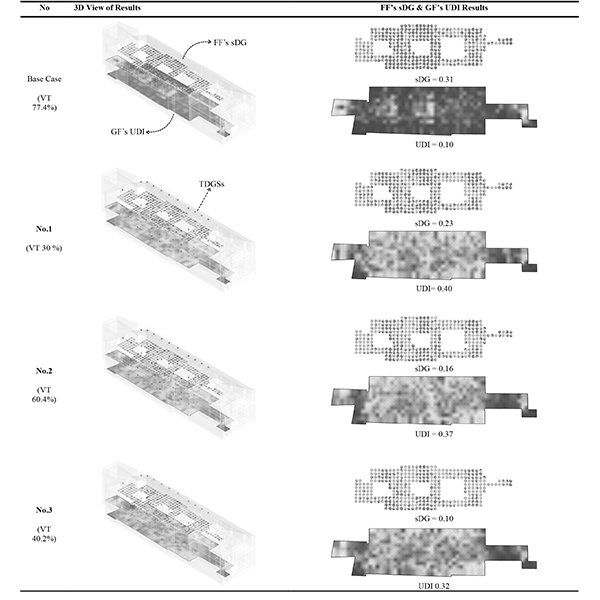
Effects of Urban Obstructions on Spatial Daylight Autonomy (sDA) and
The limited research on obstruction-driven daylight reduction continues to hinder efforts to optimize natural daylight in compact mid-rise residential buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 13 (2026) 1-19
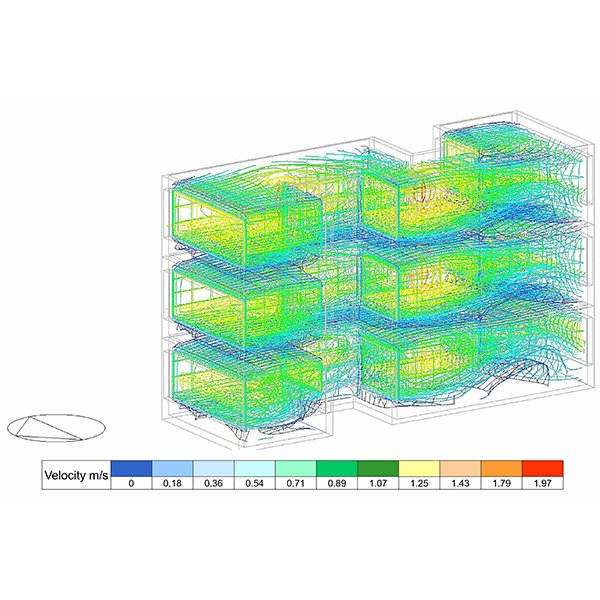
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Integration of light well through generative design to achieve optimal
A case of urban densification in heritage towns like Pondicherry has led to deep-plan wall to wall layouts, where the depth of the plot is considerably more than its width and multi-storey buildings with limited access to day light and natural ventilation.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 548-560
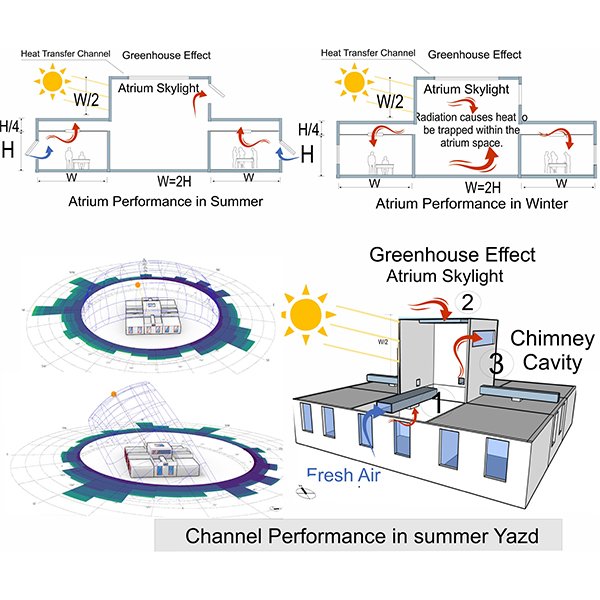
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design Optimization of Atrium Skylights for Enhanced Office Building Performance
The increasing demand for energy and the impact of climate change underscore the necessity of energy-efficient building designs. This study optimizes atrium skylights as a passive design solution for Yazd, Iran aiming to enhance thermal and visual comfort.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 520-547
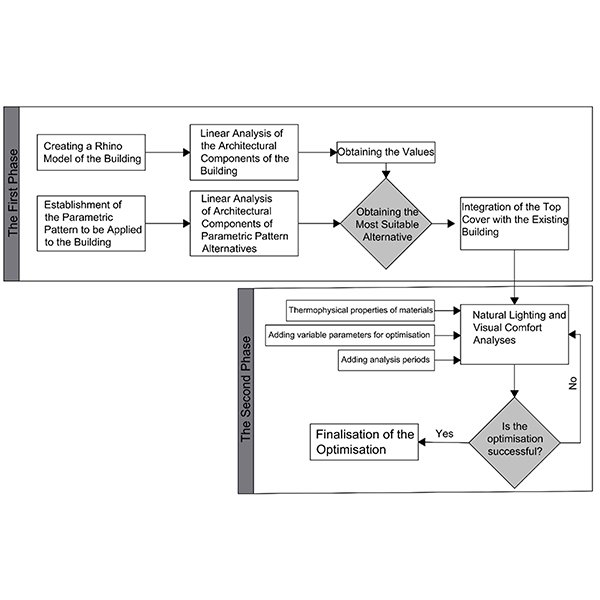
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Parametric Exploration of Natural Lighting and Visual Comfort in Contemporary
The re-functioning of historical buildings frequently necessitates new additions. This is particularly relevant for historical buildings with open courtyards, where interventions often involve the installation of upper covers using contemporary materials and techniques This issue can become especially apparent in historical buildings that are completely enclosed with transparent materials, raising concerns about the greenhouse effect and its potential to compromise indoor comfort.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 506-519
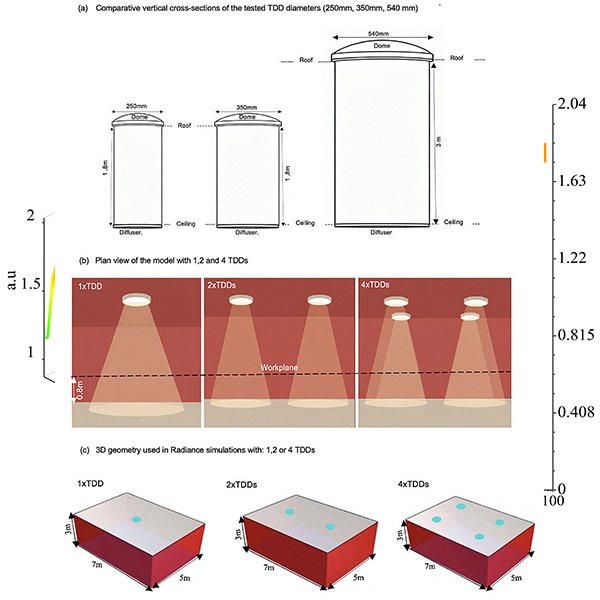
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Multi-Criteria Optimization of Tubular Daylighting Devices for Classrooms in
In educational architecture, particularly in high-solar climates, achieving a balance between ample daylight and visual comfort is a significant challenge.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 491-505
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Multi-objective Optimization of Girih Tile Patterns and Colored Glass
Efficient energy use is vital in architecture, and the building envelope plays a key role in aesthetics, thermal comfort, energy efficiency, and natural lighting.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 441-467
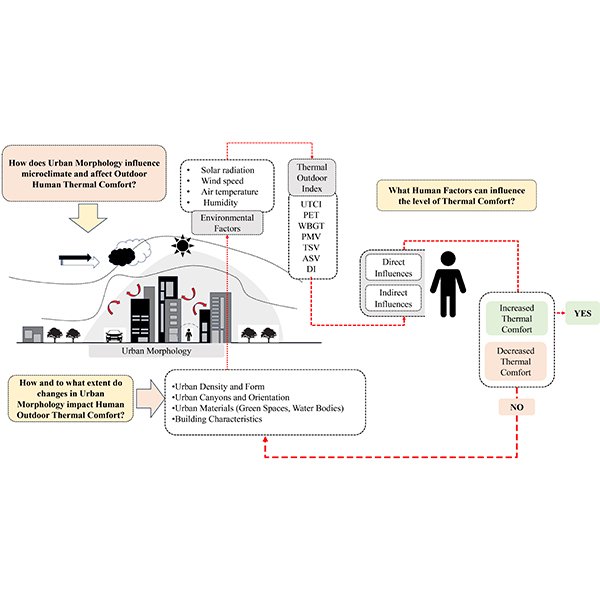
REVIEW ARTICLE
Human Interaction with Urban Morphology under the Influence of Urban
Outdoor urban spaces are essential to residents’ well-being, yet their thermal comfort is increasingly compromised by urbanization and climate change. .
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 468-490
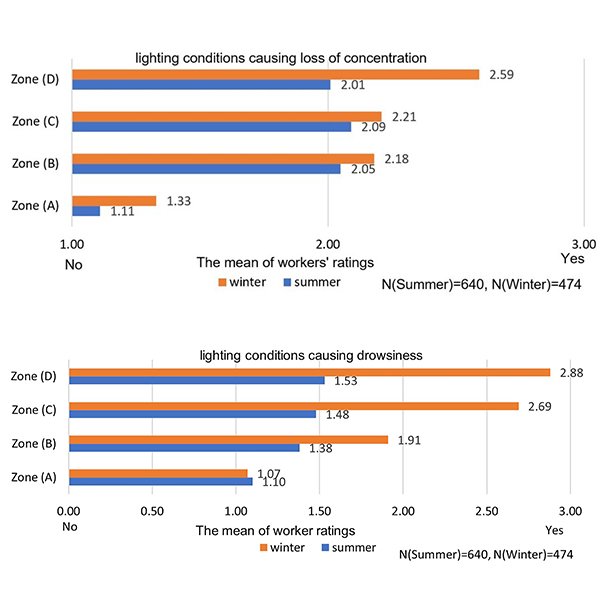
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluating the Impact of Lighting Conditions on Workers’ Safety and
Lighting is a key element of design that plays a significant role in affecting workers’ health and safety in industrial workspaces. Given the scarcity of scientific studies addressing visual environments in relation to workers health in industrial buildings, this field study was conducted to explore workers' responses to multiple lighting scenarios inside production halls on their occupational health and safety in six factories in Sadat City, Egypt. .
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 420-440
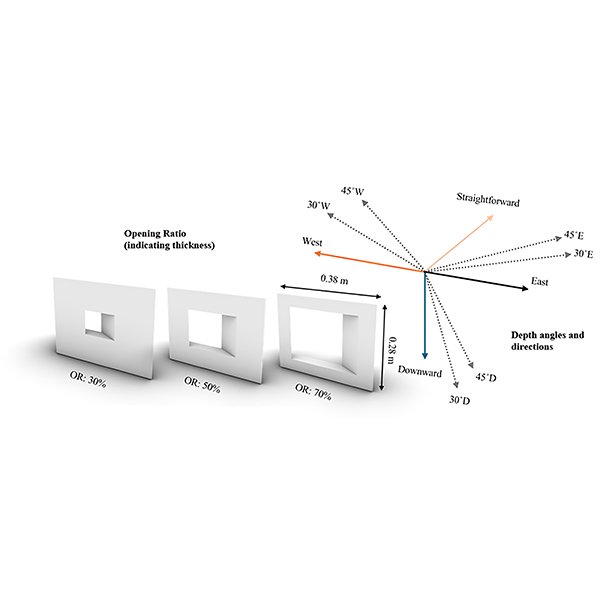
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluating Daylighting Performance of Parametric Mashrabiya in Mediterranean Climate: A
This study examines the daylighting performance of parametric Mashrabiya-inspired shading devices in a Mediterranean climate, aiming to enhance occupant comfort and visual performance.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 397-419
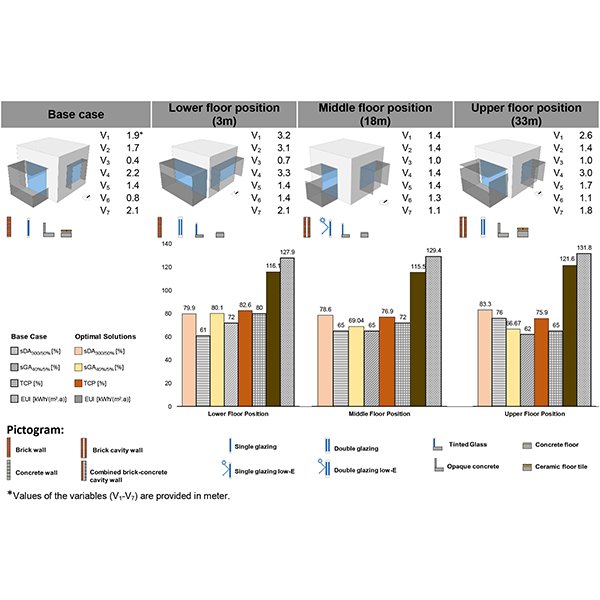
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Height-Responsive Balcony-Integrated Envelope Design for High-Rise Residential
Balconies function as essential shading elements within the building envelope, playing a critical role in regulating occupant comfort and energy efficiency.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 375-396
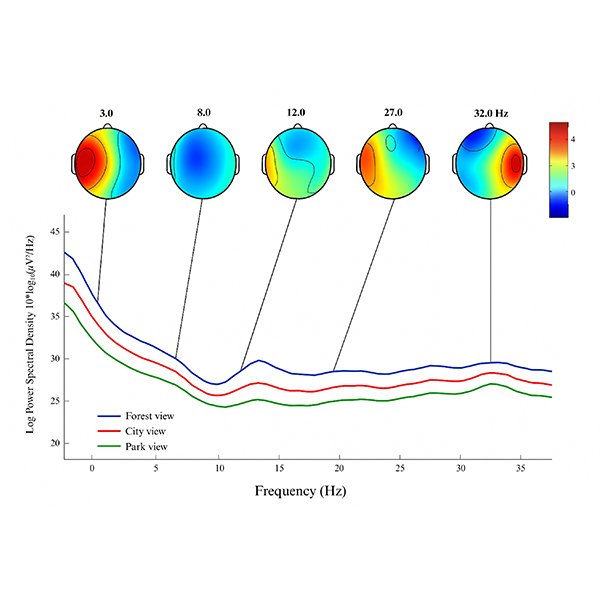
RESEARCH ARTICLE
EEG-Based Neurophysiological Responses to Classroom Window Views in Green
This study examines the neurophysiological responses of students to different classroom window views - forest, park, and city - within energy-efficient, green campus environments.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 359-374
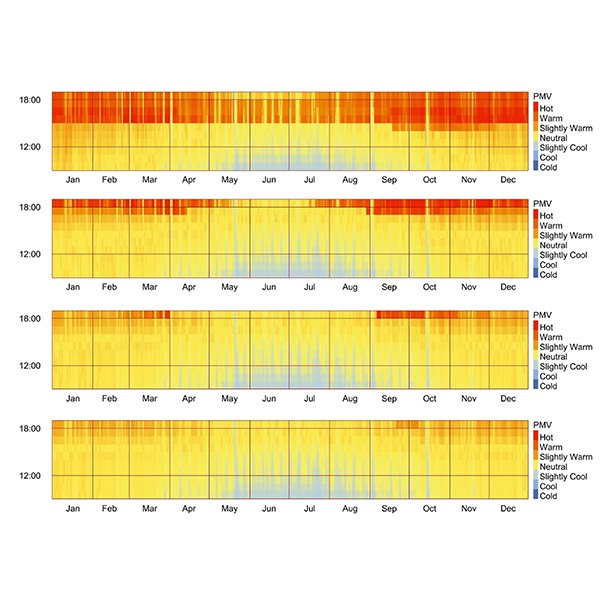
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Enhancing Year-Round Thermal Comfort with Solar Control Films: A
Windows significantly contribute to thermal discomfort in high solar irradiance climates by allowing excessive heat gains and uneven indoor temperatures.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 343-358
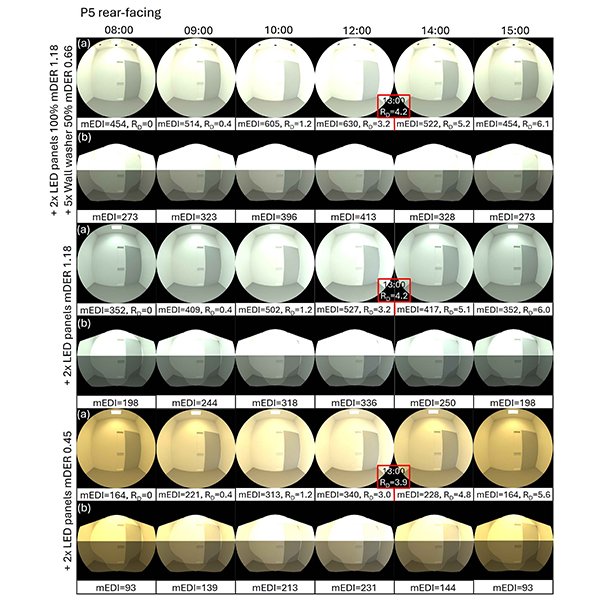
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluating Visual and Beyond-Vision Light Effects and Energy Consumption
Light influences human physiology and psychology through visual and beyond-visual effects, collectively termed ‘integrative lighting.’ Human responses depend on luminous (quantity, spectrum, directionality) and temporal (timing, duration, history) factors, yet no studies examined their combined influence on integrative lighting. Th.
Journal of Daylighting 12 (2025) 306-342

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design Alternatives of Light Shelves using Altmann Linkage
This paper proposes a novel new light shelf design with Altmann linkage using its kinetic principles: geometry and rotational angles. As previous studies explain a light shelf’s design in two ways: static and movable, the proposed one in this study has the potential to track the path of the sun due to its diagonal movement. .
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 391-407
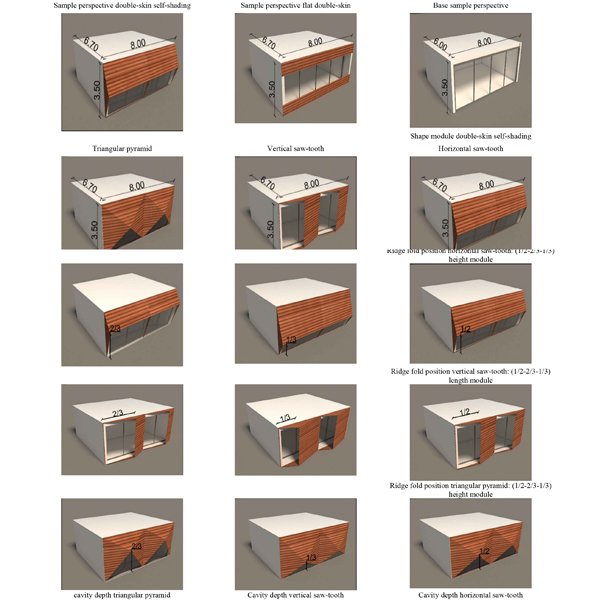
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimum Geometry of Double-skin Self-Shading Facade of Classrooms
The significant energy consumption in educational spaces worldwide and its environmental impact greatly influence the quality of space, learning levels, and student comfort.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 372-389
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Parametric Optimization Approach to Evaluate Dynamic Shading Within Double-Skin
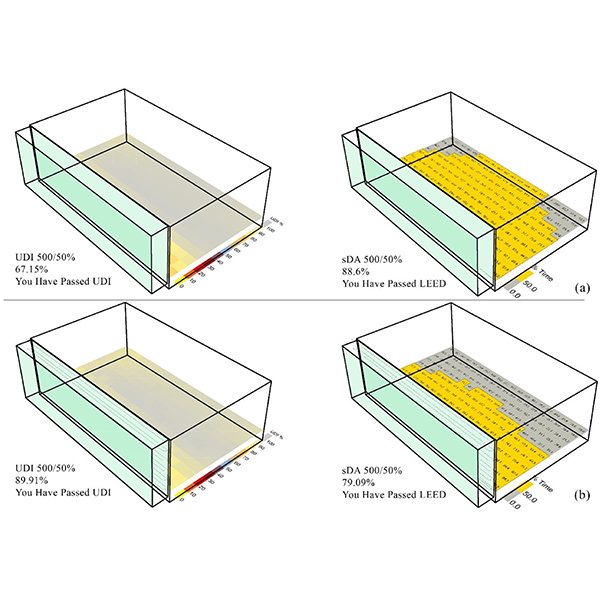
This research aims to support the choice of an appropriate dynamic louver shading system (DL-SS) within double-skin facade insulated glazed units (DSF-IGUs) as a high-performance integrated window system (DSF-IGUs/DL-SS) that meets both thermal and energy performance via daylight availability under a tropical climate.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 349-371
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Artificial Neural Network to Predict Curvature Light Shelf Design Related
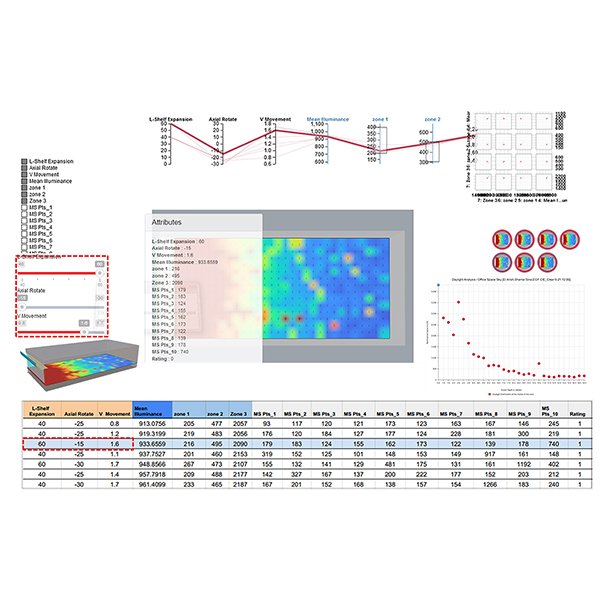
Energy Optimization in building design field now has been revolutionized due to AI and machine learning applications. Leveraging daylight to reduce artificial lighting consumption holds promise for significant energy savings, yet the nonlinear nature of daylight patterns poses challenges in prediction and optimization.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 334-348
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Investigation of the Effect of Parametric Patterned Façade and
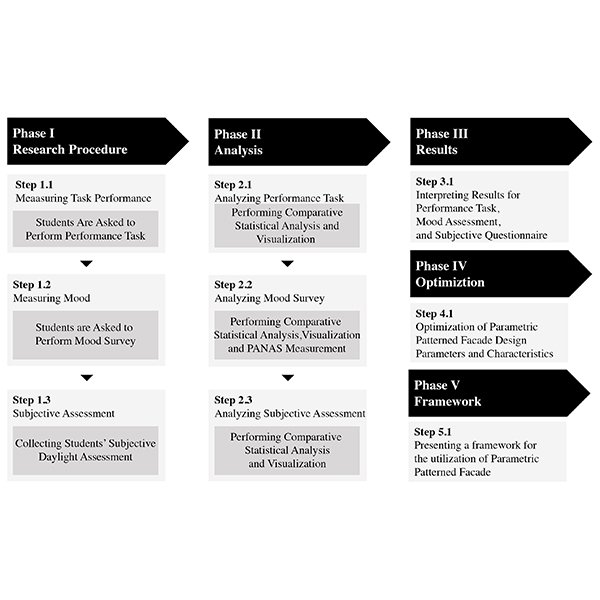
Parametric design is one of the thriving contemporary architectural treatments that not only has an influence on the design of building envelopes but is capable of affecting the users physically and psychologically.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 312-333
RESEARCH ARTICLE
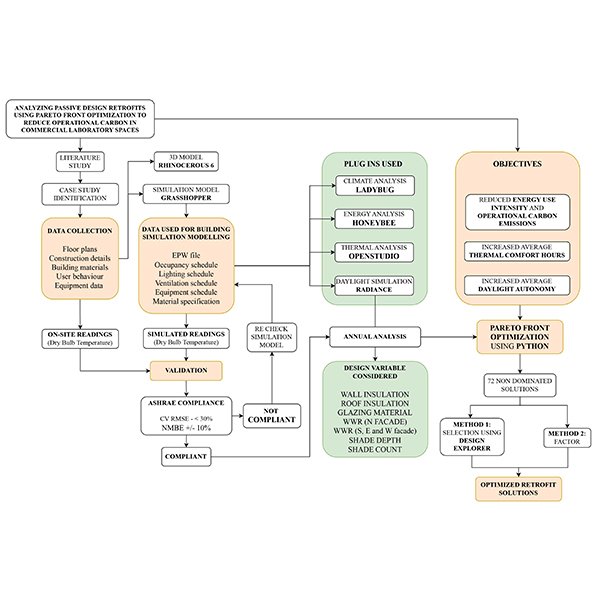
Analyzing Passive Design Retrofits using Pareto Front Optimization to Reduce
Buildings are one of the leading sources of carbon emissions in the world. Most of the carbon emissions are released during the operation phase of the building.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 290-311
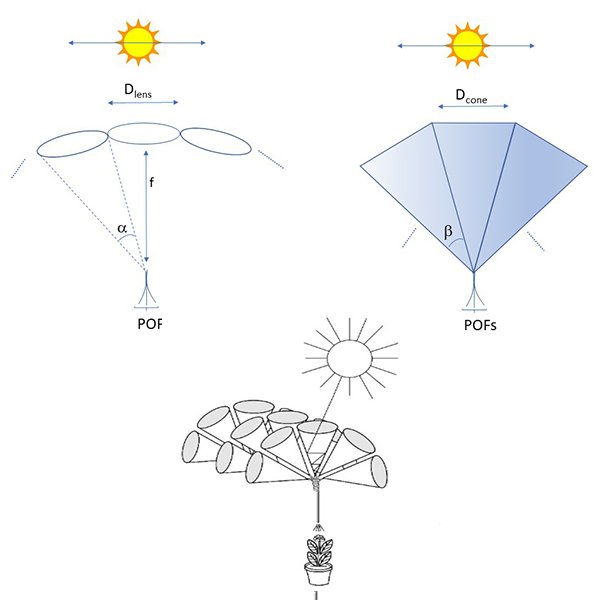
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Tracker-less Sunlight Collection Apparatus, using an Array of Optical
The paper describes an array of optical cones as a potential configuration for tracker-less daylighting, without using an electro-mechanical tracker. Subsequently, a single optical cone is analyzed, mainly in terms of sunlight collection efficiency and acceptance angle, as a function of the cone's geometrical dimensions.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 279-289
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Analytical Study on Reducing the Heating Effects of Daylight and
Climate change is an environmental issue that is rapidly escalating due to the effects of global warming. The increase in carbon emissions, along with various human activities such as industrial processes, land use changes, and the reckless consumption of natural resources, are among the primary causes of global warming.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 268-278
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimising Daylighting Performance Through Side light with Passive Devise Design
Passive lighting design plays an important role in providing natural lighting to save electricity consumption in buildings. This study aims to investigate the performance of natural lighting and the potential of alternative designs through sidelights with 3 shading device models and light shelves with different sizes in north, west, east, and south orientations.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 247-267
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylight Enhancement Strategies Through Roof for Heritage Buildings
Enhancing daylighting in heritage buildings is a complex challenge that requires a delicate balance between preserving architectural integrity and improving visual comfort.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 234-246
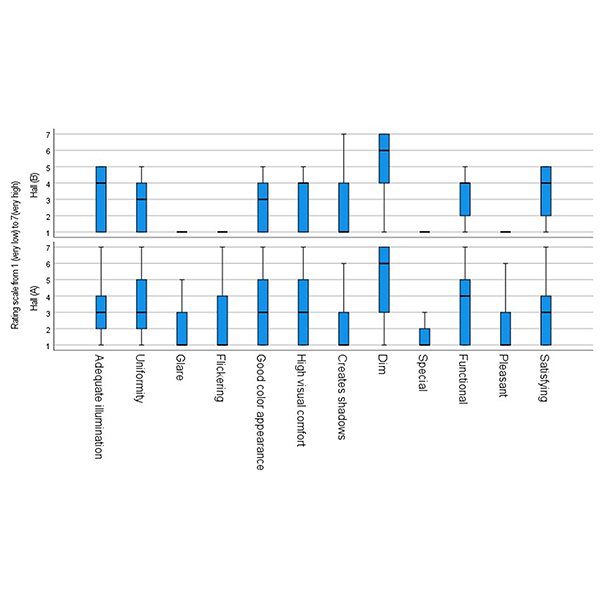
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Investigation of daylight availability in university dining halls: A case
This study evaluates the availability of daylight inside a university’s dining halls over two days (one sunny and one cloudy) using light meters in real-life sittings. .
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 216-233
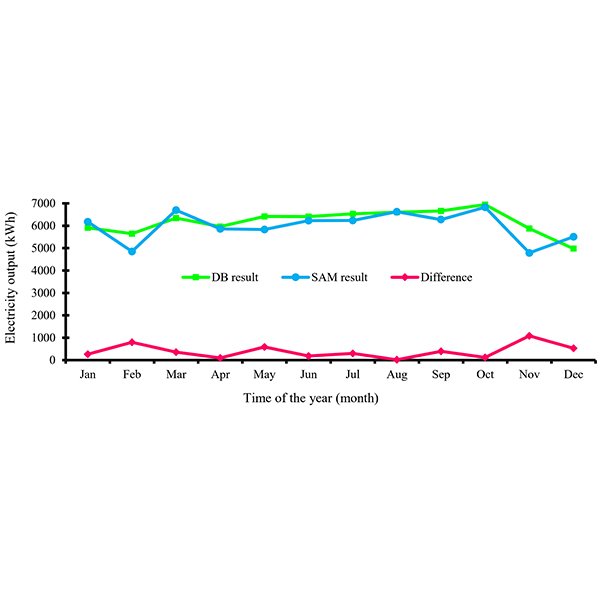
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Energy efficiency in smart schools using renewable energy strategy
As smart schools increasingly rely on technology, achieving energy efficiency becomes crucial for cost reduction and sustainability. This study investigates energy efficiency strategies in smart schools, focusing on the integration of renewable energy technologies.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 203-215
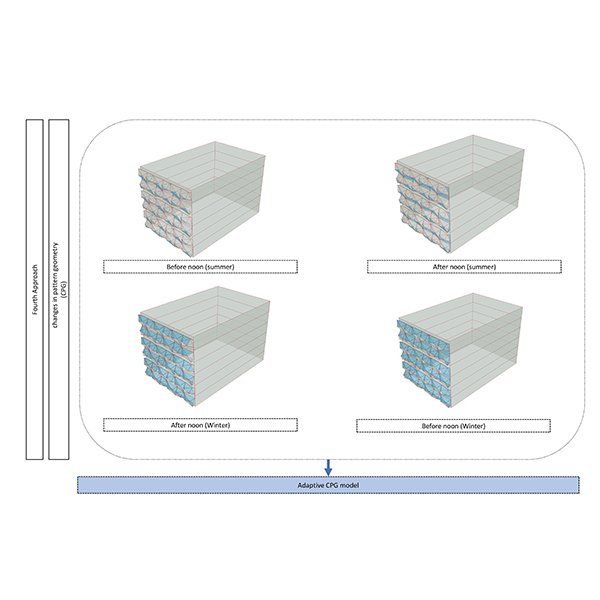
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Synergistic Strategies: Comparing Energy Performance in Climate-Adaptive Building Envelopes
Climate change and improving building energy performance are significant contemporary concerns. Conversely, climate-adaptive building envelopes (CABEs) offer promising solutions to enhance structural performance amidst fluctuating environmental conditions.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 181-202
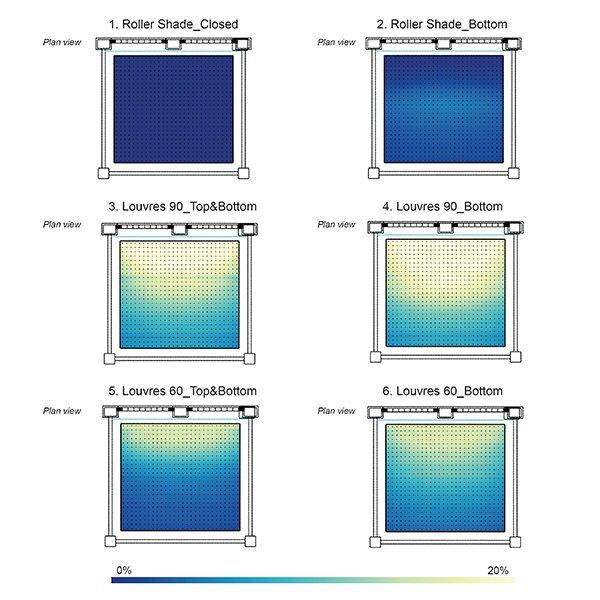
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design Adjustments For Daylighting and Visual Comfort in a Classroom
This paper evaluates how design adjustments applied to roller shades and louvres (namely the height of the shadings head and the angles of the louvre slats) can improve their annual and spatial effectiveness to provide autonomous daylight levels, reduce daylight glare problems, and offer views outside.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 165-180
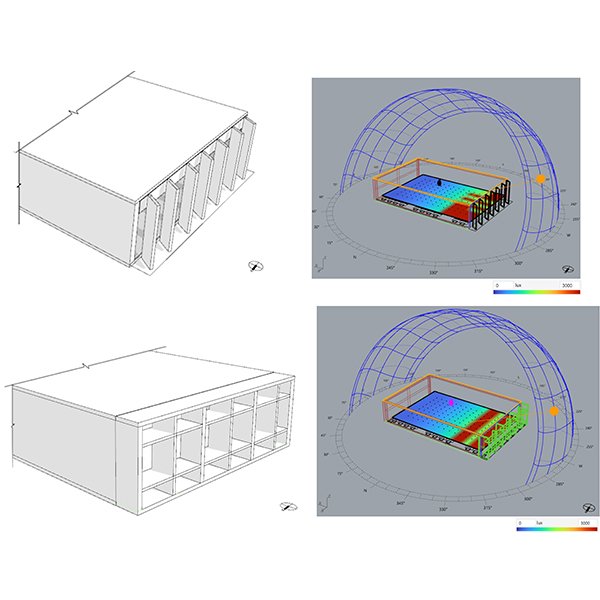
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Performance of Shading Against West Glass Facades to Optimise Daylight,
In tropical urban areas, the vertical facades of buildings often play a crucial role in capturing solar radiation and heat, especially for office buildings facing west during the afternoon.
Journal of Daylighting 11 (2024) 131-148
Join our Editorial Board
CVs should be submitted electronically to jd@solarlits.com.
Editorial Board

Dr Valerio Roberto Maria LO VERSO
Politecnico di Torino (Polytechnic University of Turin), Italy

Dr Paola Sansoni
CNR-INO, Italy

Dr Ferdinando Salata
University of Rome, Italy

Dr. Kacem Gairaa
center for renewable energy development, Algeria

Prof Umberto Berardi
Politecnico di Bari, Italy

Prof Francesco Asdrubali
University of Perugia, Italy

Dr Boon Han Lim
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Malaysia

Prof. Lambros T. Doulos
Hellenic Open University, Greece

Prof. Yuehong Su
University of Nottingham, UK

Prof Laura Bellia
University of Naples Federico II, Italy

Dr Guiqiang Li
University of Science and Technology of China, China

Prof Hongfei Zheng
Beijing Institute of Technology, China

Dr Arsenio Barbón
University of Oviedo, Spain

Prof. Nabil Elminshawy
Port Said University, Egypt

Prof. Önder Güler
Istanbul Technical University, Türkiye

Dr Vincenzo Costanzo
University of Catania, Italy

Dr Hui Lv
Hubei University of Technology, China

Dr Lim Yaik Wah
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia

Dr jian yao
Ningbo University, China

Dr Hui Shen
Texas A&M University-Kingsville, USA

Faris Ali Mustafa
Salahaddin University - Erbil, Iraq

Dr Marina Bonomolo
University of Palermo, Italia

Dr. Peng XUE
Beijing University of Technology, China

Omid Nematollahi
Isfahan University of Technology, South Korea

Prof Jitka Mohelnikova
Brno University of Technology, Czech Republic

Dr Ahmed A. Y. Freewan
Jordan University of Science and Technology, Jordan

Dr Paula M. Esquivias
University of Granada, Spain

Dr Osama Mohamed Omar
University of Bahrain , Bahrain

Dr Petar Pejic
University of Niš, Serbia

Dr. Francesca Fragliasso
University of Naples Federico II, Italy
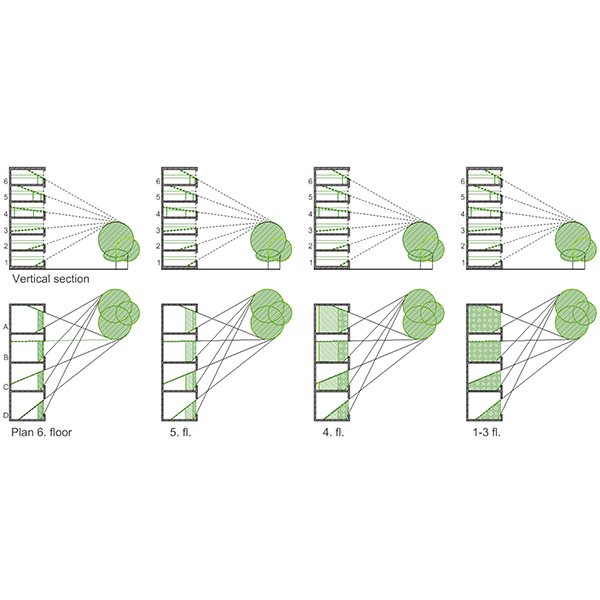
SHORT COMMUNICATION
No-Greenery Line and Greenery-View Factor, New Architectural Design
The paper proposes a new tool for evaluation of the degree of visual contact with the outdoor greenery, the Greenery-View factor (GV), intended to be easy to grasp and simple to use.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 282-286
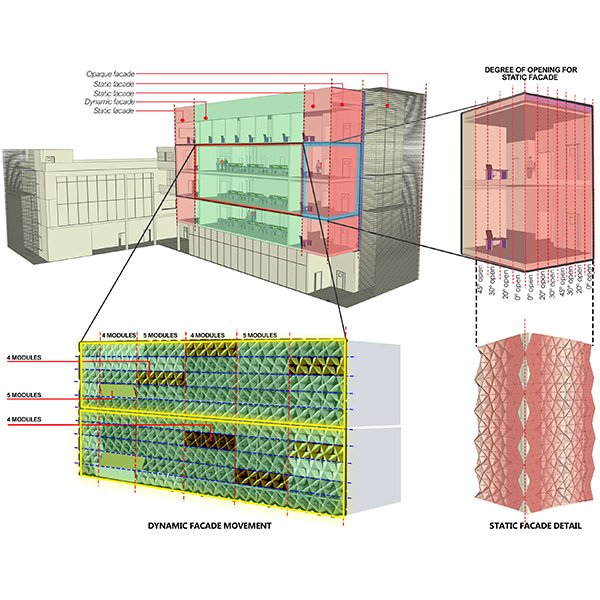
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Development of Two-Step Biomimetic Design and Evaluation Framework for
Climate change, increase in CO2 production and energy consumption are major global issues and the building, environmental and construction sector is contributing to the increasing concern day by day.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 13-27

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Development of Fresnel-based Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV) System with Uniform
Different designs have been presented to achieve high concentration and uniformity for the concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) system. Most of the designs have issues of low efficiency in terms of irradiance uniformity.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 2-7

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design Optimization of the Skylight for Daylighting and Energy Performance
In terms of sustainable design, lateral windows and skylights are important. Daylighting has become a vital component in office buildings because it increases occupants' productivity, well-being, and energy savings via windows and skylights.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 72-86

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Daylight utilization with light pipe in farm animal production: a
Light pipes, which are complex optical systems, offer a passive way to bring daylight to deep buildings, such as agricultural buildings. However, the lack of reliable performance predictability methods for light pipes represents a major obstacle preventing their widespread use.
Journal of Daylighting 3 (2016) 1-11

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Appraisal of the visual environment in an industrial factory: a
The physiological and psychological benefits of daylighting for office occupants have been well explored. Current research usually focuses on visual comfort in office buildings.
Journal of Daylighting 3 (2016) 12-26
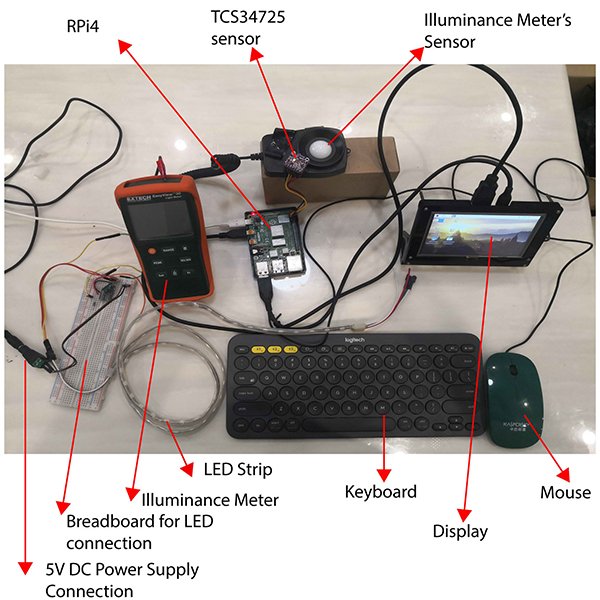
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Design and Simulation of a Circadian Lighting Control System Using
This paper introduces a fuzzy logic-based circadian lighting control system using flexibility of Light-Emitting Diode (LED) lighting technology to synchronise artificial lighting with circadian (natural) lighting Correlated Colour Temperature (CCT) characteristics.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 64-82

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Acrylic Panels Applications as Building Materials and Daylighting Devices
Enormous studies have been conducted to enhance the daylighting utilization in buildings either by direct lighting techniques, lighting reflection systems, lighting transporting systems, or by light tracking systems.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 258-272

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Outdoor Investigation of High Concentrator Photovoltaic Under Uniform and Non-
This study was performed in outdoor conditions to quantify the level of influence on the electrical performance of the Multi-junction (MJ) solar cells.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 1-12
RESEARCH ARTICLE
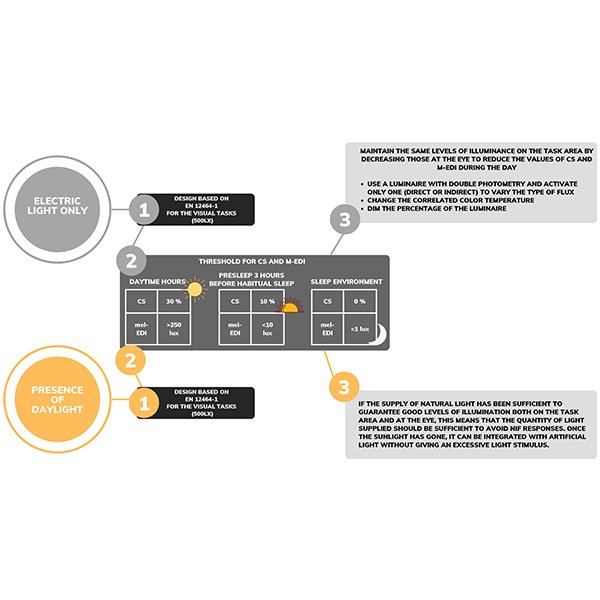
Integrative Lighting Design: How to Optimize Visual and Non-visual
The objective of this paper is to outline fundamental principles for the electric lighting design of workplace environments such as offices. The study considers both the suggested guidelines and values for non-visual light design and the specifications for visual tasks dictated by the EN 12464-1:2021.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 192-203

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optical Analysis of a New Solar Distiller with Cylindrical Surface
In this paper, a new solar distiller floating on ocean with cylindrical surface concentrator and vertical gap evaporator is proposed for solving the problem of freshwater shortage in islands.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 100-109

RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Novel Approach to Multi-Apertures and Multi-Aspects Ratio
Daylightophil architecture concept is one of the most significant ways to reduce the electrical load consumption in building sector. In deep-plan buildings, or windowless buildings, advanced light transmission systems are used to compensate lighting demands in high-performance architecture theory.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 186-200

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Visual Comfort Assessment of Hospital Patient Rooms with Climate Responsive
As advanced technologies become prevalent, they are being used more widely in numerous fields. The building sector is not an exception. One of these cutting-edge technologies is responsive facades, which are used in buildings and have an undeniable effect on daylighting.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 17-30
RESEARCH ARTICLE
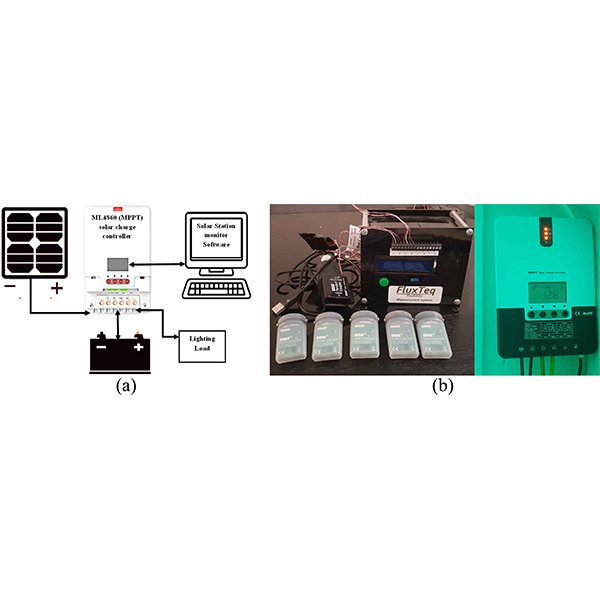
Experimental Investigation of Overall Energy Performance in Algerian Office Building
Building integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) energy has now become one of the most significant renewable energy alternatives for providing natural daylight and clean energy.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 23-41
RESEARCH ARTICLE
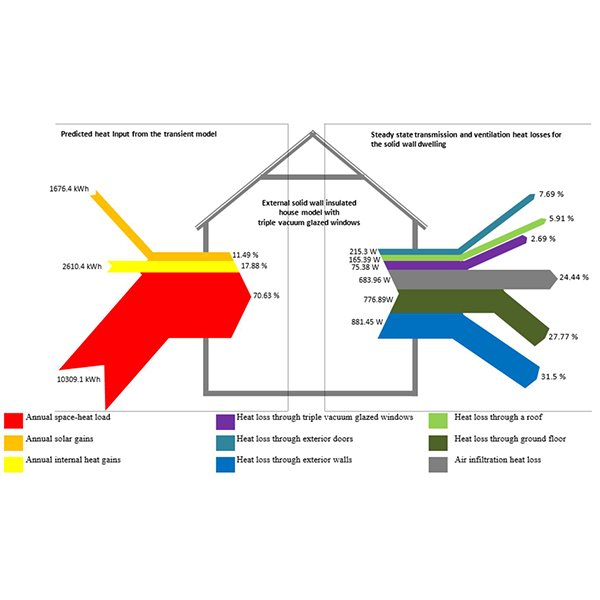
Solar Energy Gain and Space-Heating Energy Supply Analyses for
A considerable effort is devoted to devising retrofit solutions for reducing space-heating energy in the domestic sector. Existing UK solid-wall dwellings, which have both heritage values and historic fabric, are being improved but yet they tend to have meagre thermal performance, partly, due to the heat-loss through glazings.
Journal of Daylighting 4 (2017) 15-25
RESEARCH ARTICLE
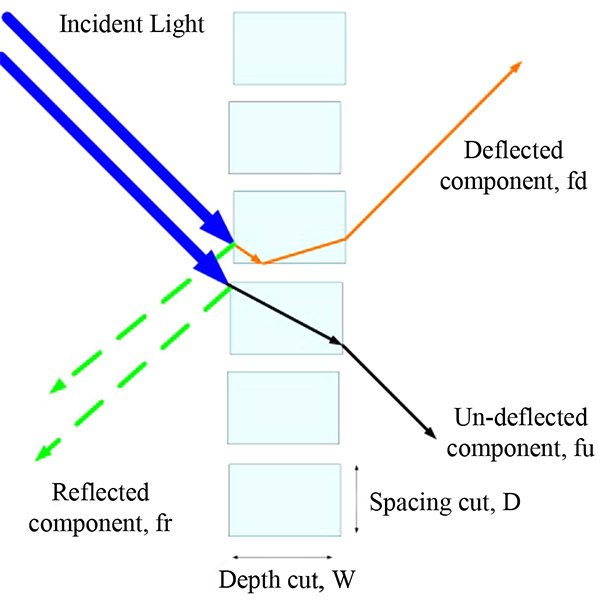
Maximizing the Performance of Laser Cut Panel by Interaction of
The interaction between different ceiling geometries with laser cut panels (LCPs) is investigated using real experiments and computer simulations to maximize the daylight performance of the LCP.
Journal of Daylighting 1 (2014) 29-35
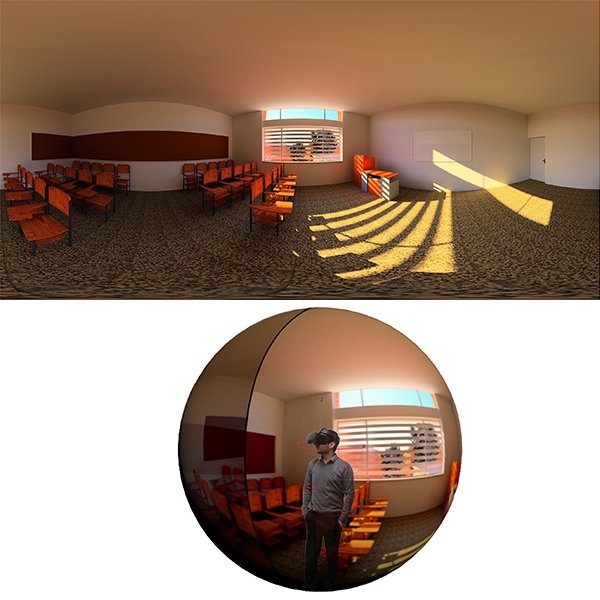

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluation of Occupants’ Visual Perception in Day Lit Scenes: A
Daylight improves indoor environmental quality, the physical and mental health of occupants, and their efficiency. Research in the area of human-centric lighting that considers the visual and non-visual effects of light on human vision, have focused on examining human visual perception in response to a wide variety of lighting aspects.
Journal of Daylighting 10 (2023) 45-59
RESEARCH ARTICLE
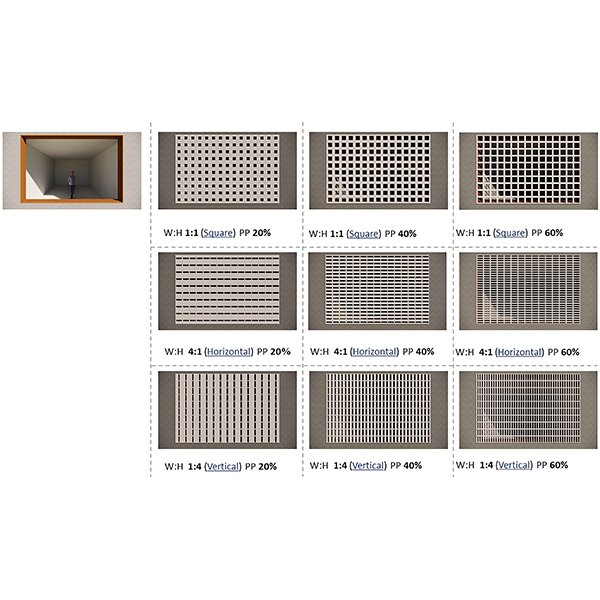
The Significance of Aperture Proportion for the Lighting Behaviour and
Traditional solar screens in Iran (called Moshabak) are architectural devices used mainly in hot-arid regions, with two interrelated functions: controlling the penetration of sunlight and gaze from outside.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 242-256

RESEARCH ARTICLE
A Survey on Daylighting Education in Italian Universities. Knowledge of
Daylighting is a strategic topic to achieve sustainable buildings, so it is more and more imperative that it is implemented in architecture curricula to prepare a new generation of daylighting-oriented practitioners.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 36-49

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimization of Daylight Performance Based on Controllable Light-shelf Parameters
This study aims to achieve a balance of daylight availability in the work-plane environments of a fully glazed facade integrated with a light shelf system using an optimization procedure that can assist architects with assessing the daylighting performance of numerous design alternatives, and build-up the optimized design.
Journal of Daylighting 7 (2020) 122-136

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optical Characteristic Investigation on an Underwater Adjustable Focus Solar Concentrator
This paper presents an underwater adjustable focus solar concentrator, which is composed of a piece of transparent elastic membrane and a hollow cylindrical-like structure.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 169-175
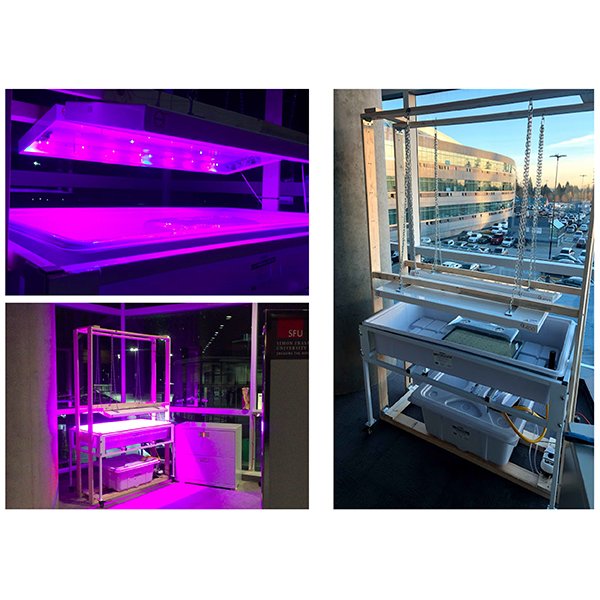

RESEARCH ARTICLE
An Intelligent IoT-enabled Lighting System for Energy-efficient Crop
In this paper, an intelligent lighting instrumentation and automation system is presented with the objective of achieving high energy-efficiency in greenhouse supplemental lighting based on the Internet of Things (IoT) technology.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 86-99
REVIEW ARTICLE
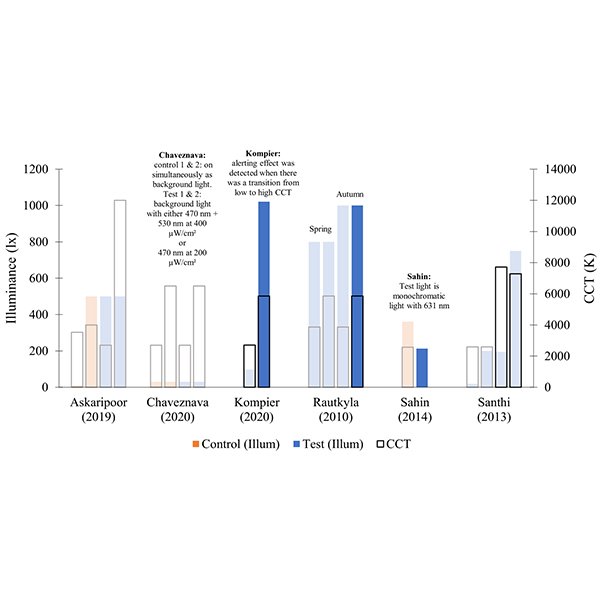
Alerting Effect of Light: A Review of Daytime Studies
Light affects humans beyond only image formation. Several studies have reported that light can increase daytime alertness and can therefore be positively utilized to counter daytime fatigue and increase productivity in workspaces.
Journal of Daylighting 9 (2022) 150-163

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Automatic vs Manual Control Strategy for Window Blinds and Ceiling
A case study to evaluate the occupants' satisfaction in relation to two different control strategies (fully automatic and manual) for blind and ceiling lights use in cell offices was carried on in Trondheim, Norway.
Journal of Daylighting 6 (2019) 112-123

RESEARCH ARTICLE
Development of a Machine-Learning Framework for Overall Daylight and
Application of machine learning methods as an alternative for building simulation software has been progressive in recent years. This research is mainly focused on the assessment of machine learning algorithms in prediction of daylight and visual comfort metrics in the early design stages and providing a framework for the required analyses.
Journal of Daylighting 8 (2021) 270-283
 HOME
HOME